Setting up a Home Server: Its Importance and Benefits Explained

Arsalan Rathore
With the rapid developments in the digital landscape, the need for home server has increased. People who love gaming, work remotely or are generally concerned about their online privacy should opt for home servers. This allows them to have control of their online presence and a whole lot options for customisations related to the server side for enhancing performance.
If you aren’t aware how to setup a home server then follow this guide. In this guide we’ve discussed all the details you should know for setting up a home server.
Table of Contents
What is a Home Server?
A home server is a dedicated computer or device set up in a residence to perform various server-related tasks. Unlike personal computers, a home server is designed to handle specific functions and services, primarily for general computing tasks.
These functions range from file storage and sharing to running a web server, hosting media content, or facilitating multiplayer gaming. The essential characteristic of a home server setup is that it operates 24/7, providing a centralized platform for managing and delivering services within your home network.
What is a Home Server Used For?
A home server serves various purposes and can be tailored to your needs. Here are some common uses for a home server:
File Storage and Sharing
One of the primary uses of a home server is to store and share files within your home network. This can include documents, photos, videos, music, and more. With a home server, you can create a centralized repository for your data, making it easily accessible from any device connected to your network. You can also set up user accounts and permissions to control who can access and edit specific files or folders.
Data Backup
Home servers are excellent for implementing automated data backup solutions. Regularly backing up your important files and system data ensures you can recover them in case of hardware failure, data corruption, or accidental deletion.
Media Streaming
Media servers are designed to store and stream multimedia content to various devices in your home. Whether you have a vast collection of movies, music, or photos, a media server can make it convenient to access and enjoy your media on smart TVs, gaming consoles, computers, and mobile devices.
Web Hosting
Setting up a web server on your home network enables you to host your own websites, blogs, or web applications. This is a fantastic opportunity to learn about web development, gain full control over your online presence, and reduce hosting costs.
Game Hosting
Gamers can benefit from a home server by using it to host multiplayer game sessions. This provides low-latency gameplay, the ability to create custom gaming environments, and the option to play with friends and family in a private, controlled setting.
Remote Access
Home servers allow you to access your data and services remotely. Whether you’re traveling or at work, you can connect to your home server to retrieve files, manage downloads, or check the status of various services. This level of remote access is not only convenient but also enhances your productivity.
Home Automation
Some enthusiasts use home servers to control and automate various aspects of their homes. For example, you can set up a server to manage smart devices, control lighting, and heating systems, or even create a home security system.
Security and Surveillance
Home servers can be used for home security, such as recording and storing surveillance camera footage. This allows you to monitor and review security footage at your convenience.
Learning and Experimentation
A home server provides a platform for learning about server administration, network management, and various software applications. It’s an ideal environment for experimenting with different services and configurations.
Privacy and Control
You have more control over your data and privacy by running your home server. You can choose which services to run, who has access, and how data is stored and secured.
Types of Home Servers
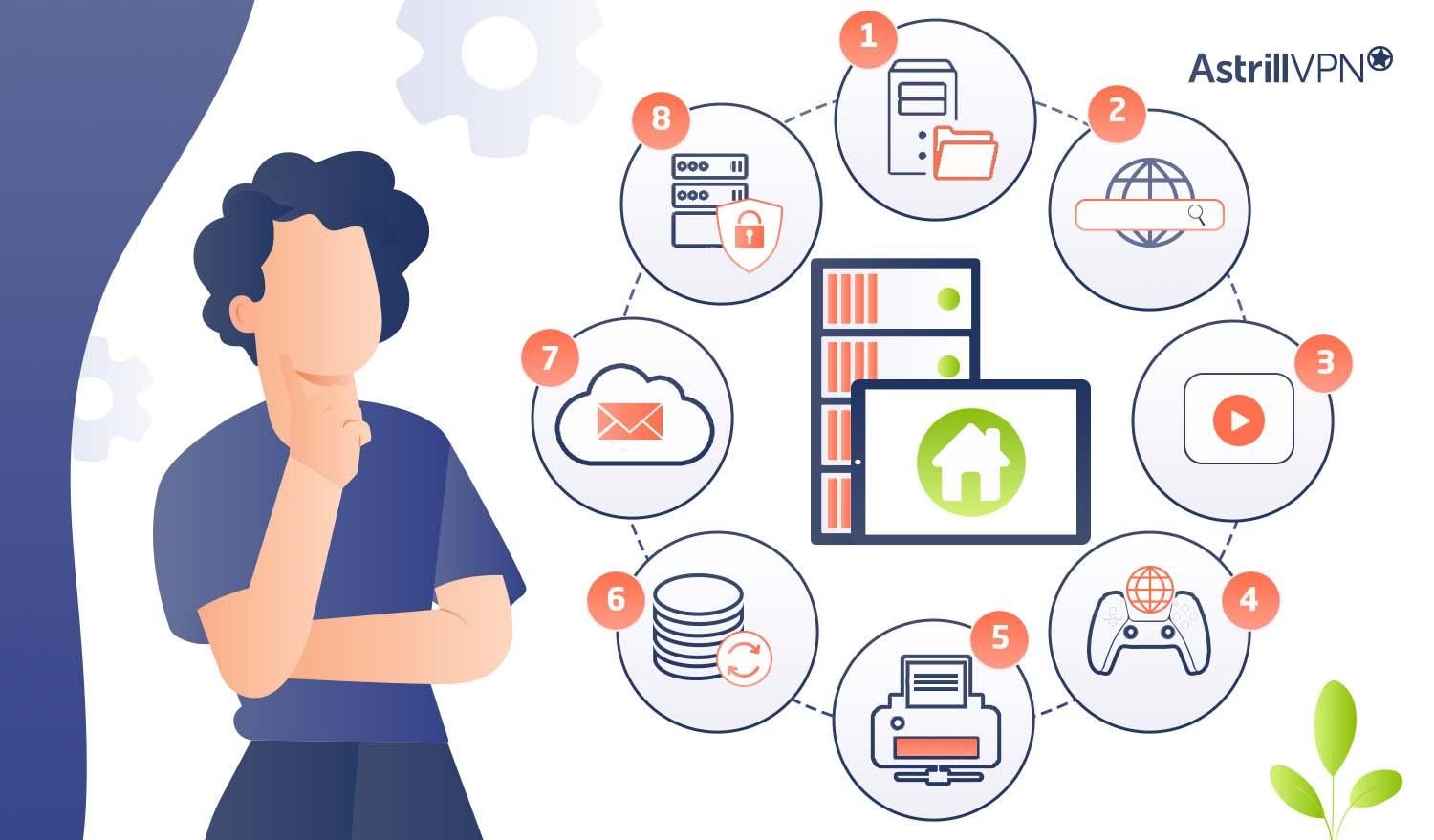
Home servers come in various forms, each designed to perform specific functions and cater to different needs within your home network. Here, we’ll explore the most common types of home servers:
1. File Server
A file server is primarily used for storing and sharing files within your home network. It is a central repository for documents, photos, videos, and other data. File servers make it easy to organize and access files from multiple devices. They often provide user accounts and permissions to control who can access and edit specific files or folders. Additionally, they can offer features like automated backup and synchronization of files across devices.
2. Web Server
Web servers host websites and web applications on your home network. This allows you to create and manage your own websites or web-based projects. You can experiment with web development, host personal blogs, showcase your portfolio, or even create a private family website. Popular web server software includes Apache, Nginx, and Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS).
3. Media Server
Media servers are designed to store and stream multimedia content within your home. They can house your music, movies, TV shows, and photos, making it easy to access and enjoy your media on various devices, such as smart TVs, gaming consoles, computers, and mobile devices. Media server software often includes features like metadata management and remote access for media streaming.
4. Game Server
Gamers can set up home servers to host multiplayer game sessions. This provides a low-latency gaming experience, full control over server settings, and the ability to create private gaming environments for friends and family. Game servers support various games, from classic titles to modern online multiplayer games. The specific server software required depends on the game you want to host.
5. Print Server
A print server manages and shares printers within your home network. It simplifies printing documents from multiple devices, eliminating the need to connect each device to the printer directly. This is incredibly convenient for households with multiple computers and devices.
6. Backup Server
A backup server specializes in automating data backups from various devices on your network. It can be configured to back up files, system images, or even databases, ensuring that your critical data is protected in case of hardware failure, data corruption, or accidental deletion.
7. Email Server
An email server allows you to run your email system within your home network. This can be a privacy-focused alternative to using commercial email services. You can create and manage your email accounts and fully control your email communication.
8. Proxy Server
A proxy server acts as an intermediary between your devices and the internet. It can be used for various purposes, such as improving security, privacy, and performance. Some users set up proxy servers to filter web content, control access, or enhance online anonymity.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Home Sever
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Centralized data storage | Initial cost |
| Data backup and recovery | Maintenance and upkeep |
| Media streaming | Increased power consumption |
| Web hosting | Technical expertise required |
| Gaming and customization | Security risks if not configured properly |
| Remote access | Noise and heat generation |
| Privacy and control | Potential impact on internet speed |
| Cost savings over time | Space requirements for server hardware |
| Learning opportunity | Legal considerations from ISPs |
| Hardware compatibility challenges |
What Equipment Do You Need to Set up a Home Server?
Setting up a home server requires specific equipment to ensure its proper functionality. Here’s a list of essential equipment you’ll need to set up a home server:
Essential Hardware and Equipment
- Server Computer: You’ll require a dedicated server computer, a repurposed desktop, or a purpose-built server machine.
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Ensure the CPU can efficiently handle the server tasks you plan to run.
- Random Access Memory (RAM): Sufficient RAM is essential to support the server’s services and multitasking.
- Storage Drives: You’ll need one or more storage drives for your data. Consider using redundant drives for data safety.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): A Gigabit Ethernet NIC is recommended for high-speed network connectivity.
Operating System
Choose an appropriate server-specific or general-purpose operating system suitable for server tasks. Popular choices include Windows Server, various Linux distributions (e.g., Ubuntu Server, CentOS), and FreeBSD.
Networking Equipment
- Router: A router capable of managing network traffic, assigning IP addresses, and enabling port forwarding is essential for network connectivity.
- Network Switch: A network switch provides additional Ethernet ports for seamless networking if you have multiple devices to connect to your home server.
- Router Configuration Tools: Access to your router’s web-based configuration interface is required to set up port forwarding and dynamic DNS (if needed).
Power Management
- Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): A UPS helps protect your home server from power outages and voltage fluctuations, ensuring continuous operation and preventing data loss.
Data Backup and Storage
- External Hard Drives or Network-Attached Storage (NAS): These can serve as backup devices or additional storage for your server. NAS devices are particularly useful for their centralized and network-accessible storage capabilities.
Security Measures
- Firewall: Consider implementing a firewall to protect your home server from external threats.
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): An IDS can help monitor and safeguard your server against unauthorized access.
- Antivirus Software: Install antivirus software to protect your server from malware and viruses.
Cooling and Ventilation
Ensure proper cooling and ventilation, including fans and airflow, to maintain optimal operating temperatures for your server hardware. This is especially important for systems running 24/7.
Physical Space
- Allocate a dedicated space in your home to accommodate your server hardware. Ensure sufficient space for the server, airflow, and cable management.
- Use surge protectors or power strips to safeguard your equipment from power surges and spikes.
Data Backup and Redundancy Equipment
If data backup and redundancy are a priority, you may need additional storage devices or a Network-Attached Storage (NAS) system for backup purposes.
Network Cables
Ensure you have Ethernet cables to connect your server, router, and other devices. Make sure you have the appropriate cable length for your setup.
Peripherals
Have a keyboard, mouse, and monitor for initial setup and maintenance tasks. These may not be needed once the server is up and running.
External Internet Access
To access your server remotely, you may need a dynamic DNS service or a static IP address from your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Optional Equipment
Backup Power Generator: A backup power generator can provide uninterrupted power to your server in areas with frequent power outages.
How to Set up a Home Server?
Setting up a server at home can be a rewarding and practical endeavor. Whether you want to centralize your files, host a website, or run specific applications, here’s a step-by-step guide to help you setup your home server:
Step 1: Define Your Server’s Purpose
Before you begin, clearly define the purpose of your home server. Is it for file storage, web hosting, media streaming, or gaming? Knowing your goals will guide the setup process.
Step 2: Choose Your Server Hardware
Select or repurpose a computer for your server. Ensure it meets the hardware requirements for your chosen server role. You’ll need a CPU, RAM, storage drives, and a network card. Consider redundancy for critical data.
Step 3: Install an Operating System
Install a suitable operating system. Popular choices include Windows, Linux distributions (like Ubuntu Server or CentOS), and FreeBSD. Ensure the OS aligns with your server’s purpose.
Step 4: Configure Network Settings
Connect your server to your home network via Ethernet and configure network settings. Assign a static IP address to your server or use DHCP with a reserved IP address.
Step 5: Set Up Remote Access (Optional)
If you plan to access your server remotely, consider configuring port forwarding on your router. You may also need dynamic DNS to handle changing IP addresses.
Step 6: Install and Configure Server Software
Install and configure the necessary server software depending on your server’s purpose. For file servers, consider solutions like FreeNAS. Web servers can use Apache or Nginx. For media servers, Plex or Emby are popular. Game servers require specific game server software.
Step 7: Configure Security Measures
Implement security measures to protect your server. Set up a firewall, install antivirus software, and enable encryption where necessary. Regularly update your software and configure user access control.
Step 8: Back Up Your Data
Set up automated data backups to protect your data. Use external hard drives, Network-Attached Storage (NAS), or cloud storage solutions for redundancy and backup.
Step 9: Monitor and Maintain
Monitor the server’s performance and set up alerts for potential issues. Regularly perform system maintenance, including updates, cleaning, and addressing hardware concerns.
Step 10: Test and Optimize
Test your server’s functionality and performance. Optimize settings and configurations based on your specific requirements. Ensure it operates smoothly and efficiently.
Step 12: Document Your Setup
Maintain documentation of your server setup, including hardware specs, software configurations, and any changes made. This documentation is helpful for troubleshooting and reference.
Importance of securing a home server
Securing a home server is important, as it safeguards your data, privacy, and the integrity of your home network. Here are the reasons why securing your home server should be a top priority:
1. Protection of Personal Data
Home servers typically store significant personal and sensitive data, including documents, photos, and videos. Securing your server prevents unauthorized access and potential data breaches, ensuring the privacy of your personal information.
2. Prevention of Unauthorized Access
A secure home server protects your network from unauthorized users. Without proper security measures, hackers can gain access to your server, potentially compromising your files and even controlling your server for malicious purposes.
3. Data Integrity
Data integrity is essential to prevent data corruption or unauthorized modifications. Securing your server reduces the risk of data tampering or unauthorized alterations to your important files.
4. Protection from Malware and Viruses
Home servers are not immune to malware and viruses. Implementing security measures like antivirus software helps safeguard your server from malicious software that could damage or compromise your data.
5. Mitigation of Cyber Threats
The internet is full of cyber threats. Securing your home server reduces the risk of becoming a victim of cyberattacks, such as DDoS attacks or ransomware incidents.
6. Secure Remote Access
If you enable remote access to your server, securing it becomes crucial. Proper security measures ensure that remote access is safe and that only authorized users can connect to your server outside your home network.
7. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Depending on your location, there may be legal obligations regarding data privacy and security. Securing your server helps ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
8. Data Redundancy and Backups
Secure servers are less prone to data loss due to unauthorized access or corruption. This helps maintain the integrity of your backups and ensures that your data is consistently protected.
9. Network Stability
Security breaches on your server can disrupt your home network, causing connectivity issues and potential downtime. A secure server contributes to the overall stability of your network.
10. Peace of Mind
Knowing that your home server is secure provides peace of mind, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of your server without constantly worrying about potential security threats.
How to Secure a Home Server with AstrillVPN
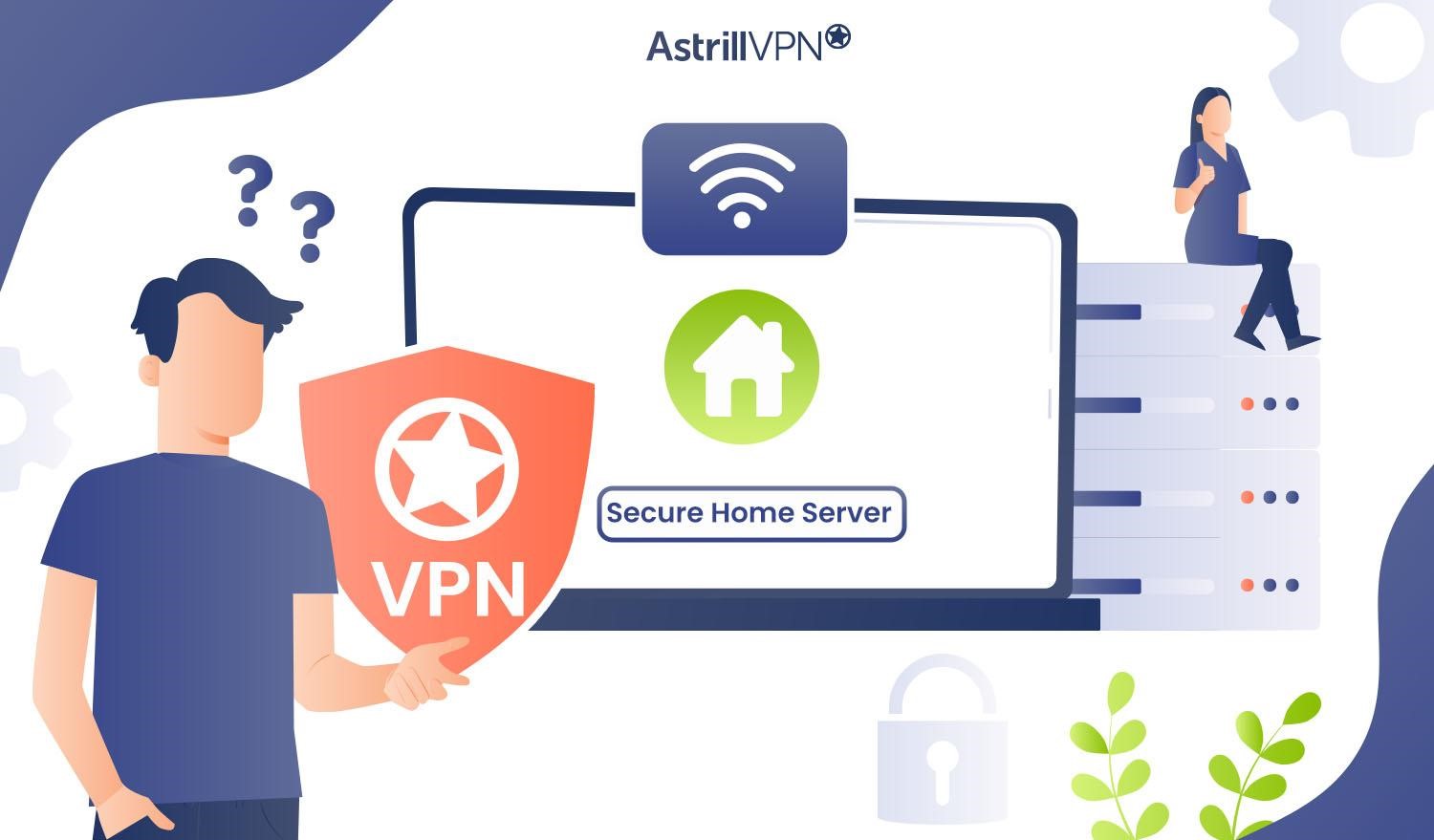
Ensuring the security of your home server is crucial for safeguarding your sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of your digital space. A secure home server protects against unauthorized access and shields your network from potential threats and cyberattacks.
You can create a resilient defense against data breaches and privacy intrusions by implementing robust security measures.
One effective way to enhance the security of your home server is by installing AstrillVPN. A VPN encrypts the communication between your server and the internet, adding extra protection against prying eyes.
AstrillVPN, in particular, offers features like military-grade encryption and secure tunneling, ensuring that your data remains confidential and secure during transmission. By anonymizing your online activities, a VPN shields your server from potential threats, making it a valuable tool for comprehensive security.
In addition to VPN protection, it’s essential to follow best practices such as regular software updates, strong password implementation, and firewall configuration. These measures collectively contribute to a well-rounded security posture for your home server.
By prioritizing the security of your server, you not only protect your personal data but also create a safer and more resilient digital environment for all connected devices.
FAQs
Yes, you can use your computer as a server. Many home servers start with repurposed desktop computers, which can be configured to perform server functions.
It depends on your needs. A home server is beneficial for centralized data storage, media streaming, web hosting, and more. A home server can be advantageous if these functionalities align with your requirements.
The cost of a secure server varies based on factors such as hardware specifications, security features, and software requirements.
Yes, you can run a server on a laptop. However, laptops may have limitations in terms of hardware and constant uptime compared to dedicated server hardware.
The cost of a server depends on factors like its purpose, specifications, and brand. Entry-level servers can start at a few hundred dollars, while enterprise-grade servers with advanced features can cost several thousand dollars.
A server is a broader term referring to a system that provides services or resources to other devices on a network. A NAS (Network-Attached Storage) is a server dedicated to file storage and sharing. All NAS devices are servers, but not all are NAS, as servers can perform various functions beyond storage.
Yes, a NAS is a type of server. It is specifically designed for storing and sharing files over a network, typically offering centralized and accessible storage for multiple devices.

No comments were posted yet