iPhones are widely regarded for their robust security features and the stringent control exercised by Apple over the iOS ecosystem, the question remains: Can you get a Trojan virus on an iPhone?
Trojan viruses, a common form of malware, have long been associated with attacks on traditional computers. However, the evolving landscape of cybersecurity has seen cybercriminals adapt their tactics to target mobile devices, including iPhones.
In this guide we have thoroughly discussed what is trojan virus, and whether your iPhone can get a Trojan or not. So without further ado, let’s get right to it!
Table of Contents
What Is a Trojan Virus on iPhone?
A Trojan virus, often called a Trojan, is a sophisticated form of malware that can infect iPhones and other devices. Named after the Greek mythological story of the Trojan horse, these malicious programs disguise themselves as legitimate and harmless software or files to infiltrate your device.
While iPhones are generally considered more secure than many other devices due to Apple’s stringent control over the iOS ecosystem, Trojans can still pose a potential risk.
Trojans belong to the broader category of malware, and they come in various forms and can perform a wide range of malicious activities on your iPhone. Understanding what Trojans can do is crucial for safeguarding your device and data.
What Do Trojans Do?
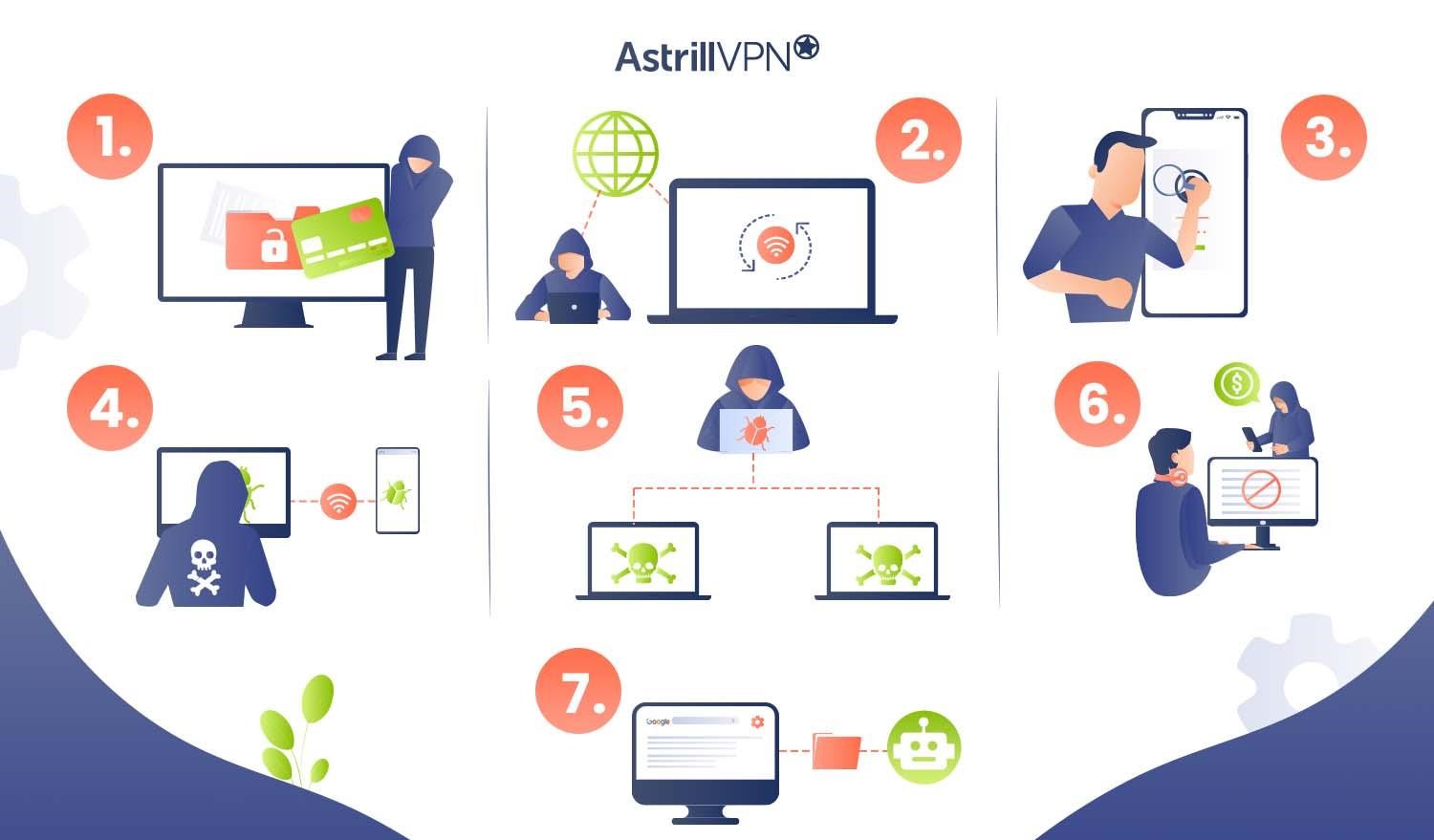
Trojans are versatile and can execute numerous malicious actions on your iPhone, compromising your security and privacy in the process:
1. Data Theft
Trojans are often designed to pilfer sensitive information stored on your iPhone. This can encompass a broad spectrum of data, including personal information, login credentials, banking details, etc. Once in possession of such data, cybercriminals may employ it for identity theft, financial fraud or even sell it on underground markets.
2. Remote Control
Some Trojans provide attackers with remote access to your iPhone. This means malicious actors can gain control over your device, accessing files and settings without your knowledge or consent. This level of intrusion allows cybercriminals to monitor your activities, steal data, or perform further malicious actions.
3. Spying
Trojans can covertly activate your iPhone’s camera and microphone, turning your device into a surveillance tool. This invasion of privacy enables cybercriminals to eavesdrop on your conversations, capture video footage, or take pictures without your awareness.
4. Propagation
Trojans often attempt to spread to other devices or networks. For instance, a Trojan might seek to propagate within the network if your iPhone is connected to a corporate network, infecting other devices or servers. This lateral movement can lead to more extensive security breaches.
5. Botnet Recruitment
Certain Trojans are crafted to enlist your device into a botnet—a network of compromised devices controlled by a single entity. Botnets can be harnessed for various malicious activities, including launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks on websites or services, sending spam emails, or carrying out other cyberattacks.
6. Ransomware
While Trojan virus on iphone is very rare compared to other platforms, Trojans can still deliver ransomware payloads. Ransomware encrypts your files, rendering them inaccessible, and demands a ransom for decryption. Falling victim to a ransomware attack can result in significant data loss and financial extortion.
7. Resource Drain
Trojans can consume your iPhone’s resources, causing it to slow down, overheat, or rapidly deplete its battery. This resource drain can make your device virtually unusable and frustrating to operate.
Types of Trojan
Trojans can be categorized into several types based on their primary functions and objectives. Here are the most common types of Trojan viruses:
1. Remote Access Trojans (RATs)
Remote Access Trojans are designed to provide attackers with unauthorized remote access to an infected device. Once inside, cybercriminals can control the device, view files, capture keystrokes, and even activate hardware components like cameras and microphones. RATs are often used for espionage, data theft, or taking full control of a compromised system.
2. Data-Stealing Trojans
Data-stealing Trojans, or Information Stealers, focus on exfiltrating sensitive information from infected devices. This includes personal data, login credentials, financial information, and more. These Trojans often target specific data types, such as credit card numbers or login details, which they can use for identity theft or financial fraud.
3. Banking Trojans
Banking Trojans are a subset of data-stealing Trojans targeting online banking and financial institutions. They aim to intercept and steal banking login credentials, account information, and transaction data. Some well-known examples include Zeus (Zbot) and Dyre.
4. Ransomware Trojans
Ransomware Trojans are Trojans that deliver ransomware payloads. Once inside a system, they encrypt the victim’s files and demand a ransom for the decryption key. Victims are often faced with the difficult choice of paying the ransom or losing access to their essential data. Notable ransomware Trojans include Locky and Ryuk.
5. Rootkit Trojans
Rootkit Trojans are designed to create hidden and privileged access points, known as rootkits, within an infected device’s operating system. These access points allow cybercriminals to maintain persistent control over the system, making detecting and removing the Trojan challenging. Rootkits can be used for various malicious purposes, including data theft and remote control.
6. Trojan Downloaders
Trojan Downloaders are trained to download and install other malware onto the victim’s device. They serve as a gateway for attackers to introduce additional malicious software, such as ransomware or keyloggers, onto the compromised system.
7. Backdoor Trojans
Backdoor Trojans, often called Backdoors, create hidden entry points (backdoors) in an infected system, allowing cybercriminals to access the system covertly. Backdoors are typically used for remote control, data theft, or launching secondary attacks on other devices or networks.
8. FakeAV (Fake Antivirus) Trojans
FakeAV Trojans masquerade as legitimate antivirus or security software. When installed, they trick users into believing their system is infected with malware, prompting them to purchase fake security solutions. These Trojans are the actual threat, deceiving users for financial gain.
How to Identify a Trojan Virus on iPhone
Detecting a Trojan virus on iPhone is essential for safeguarding your device and data. While iPhones are generally more secure than many other devices, it’s still possible for Trojans to infiltrate them. Here’s how to identify a Trojan virus on your iPhone:
1. Monitor Device Performance
Pay close attention to your iPhone’s performance. If you notice sudden and significant slowdowns, app crashes, or overall sluggishness, it could be a sign of malware, including Trojans.
2. Battery Drain
Keep an eye on your device’s battery life. A sudden and unexplained decrease in battery performance may indicate that a Trojan is running in the background, consuming resources.
3. Data Usage Analysis
Regularly review your data usage statistics in the Settings app. Unexpected spikes in data consumption may suggest that malware is transmitting data from your device without your consent.
4. Pop-Up Ads and Unwanted Notifications
Be wary of persistent pop-up ads and notifications on your device, especially when you’re not using a web browser or specific apps. Trojan-infected devices often exhibit this behavior.
5. Check Installed Apps
Review the list of installed apps on your iPhone. If you come across unfamiliar or suspicious apps that you didn’t intentionally install, it’s a red flag. Delete any such apps immediately.
6. Browser Behavior
Pay attention to your web browser’s behavior. It signifies a potential Trojan infection if it frequently redirects you to unfamiliar or potentially malicious websites.
7. App Permissions
Examine the permissions requested by your installed apps. Be cautious if an app seeks unnecessary or intrusive permissions, as Trojans may exploit these permissions to carry out malicious activities.
8. Overheating Issues
If your iPhone consistently feels hot to the touch or overheats more than usual, it could be due to a Trojan using excessive system resources.
9. Unexpected Texts or Calls
Monitor your phone bill for unexpected charges related to premium-rate texts or calls, which malware could initiate without your knowledge.
10. Security Alerts
Take security warnings or alerts that appear on your device seriously. Pay attention to these messages, as they may indicate a security issue.
11. Unusual Background Processes
Check for unusual background processes or applications running on your device. Access the “Settings” app, go to “Privacy,” then “Location Services,” and review which apps have access to your location data.
How To Remove Malware From iPhone
Removing malware from an iPhone is a crucial process to safeguard your device and data. Follow these steps to remove malware from your iPhone:
Step 1: Before attempting to remove malware, it’s important to isolate the infected device from your network and other devices to prevent the spread of the malware.
Step 2: Try to determine the specific malware affecting your iPhone. While iOS is relatively resistant to malware, knowing the type of malware can help you understand the extent of the threat and the potential risks involved.
Step 3: Make sure your iPhone is running the latest version of iOS. Apple regularly releases updates that include security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
To update your iOS:
- Open the “Settings” app.
- Scroll down and select “General.”
- Tap “Software Update.”
- If an update is available,
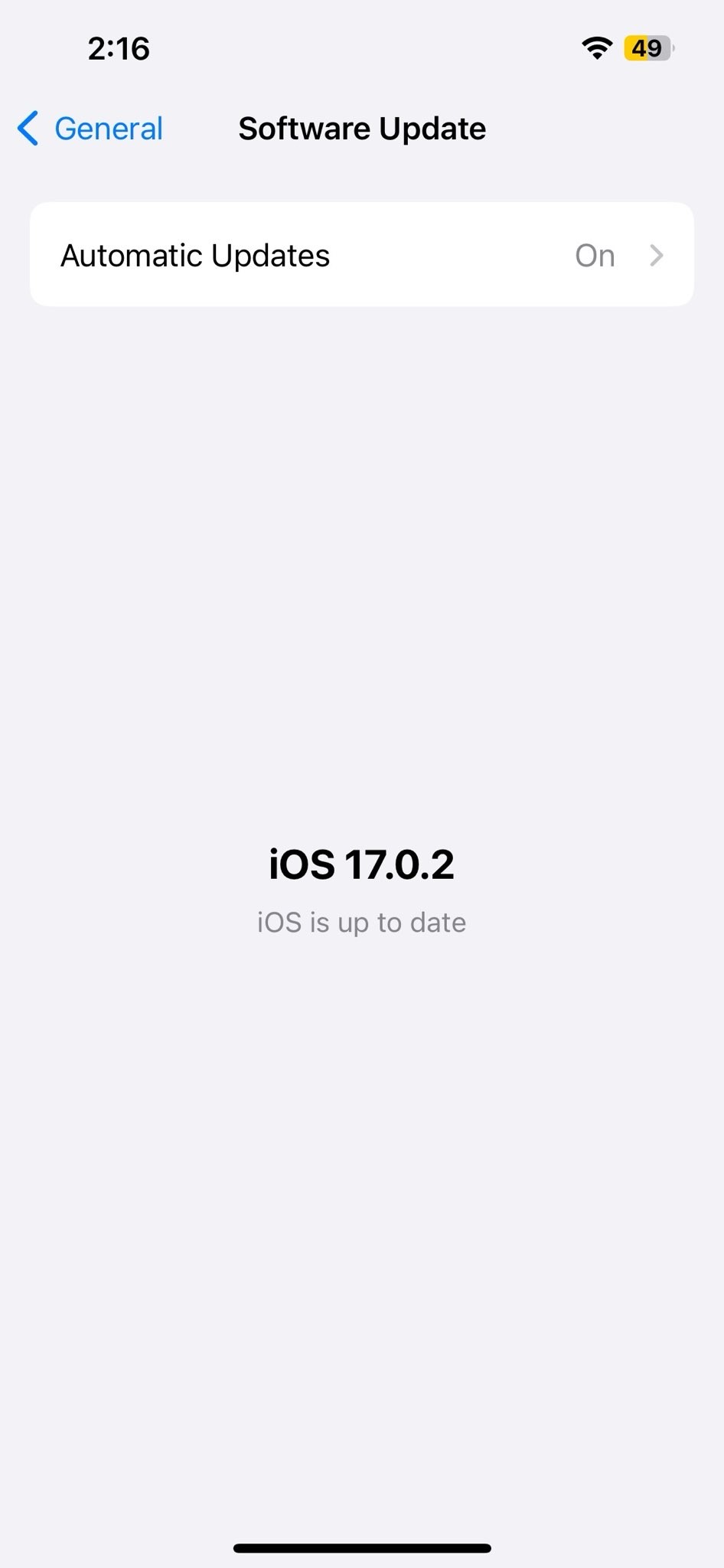
- tap “Download and Install.”
Step 4: Review the list of installed apps on your iPhone and delete any apps that you suspect may be responsible for the malware.
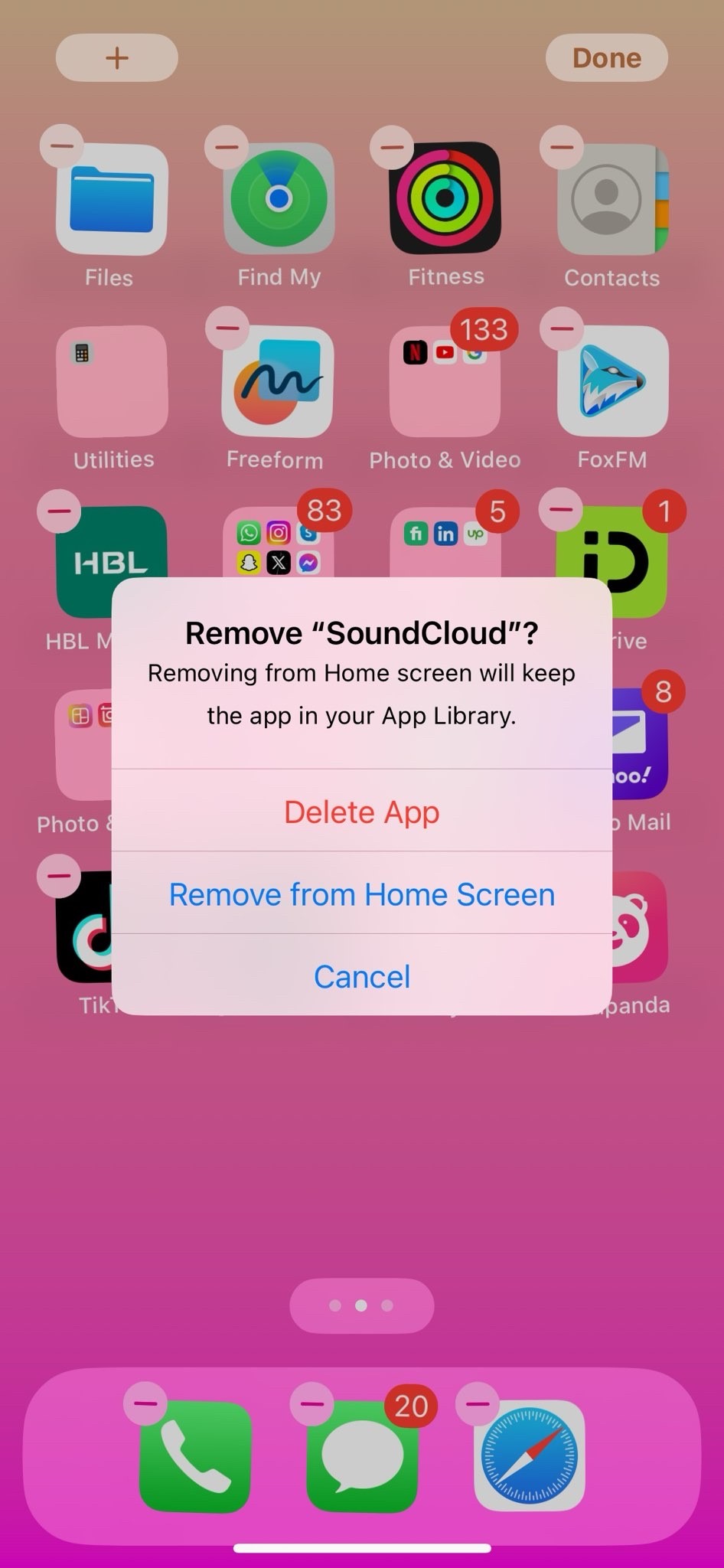
To delete an app on your iPhone:
- Press and hold the app icon on the home screen.

- When the app icons start to jiggle, tap the “X” icon on the app you want to delete.
- Confirm the deletion.
Step 5: Download and install a reputable antivirus or security app from the App Store. These apps can help identify and remove malware from your device.
Step 6: After installing the antivirus app, run a full system scan to detect and remove any malware. Follow the app’s instructions for initiating a scan.
Step 7: Change your passwords for online accounts, especially if you suspect that any of them have been compromised. Use strong, unique passwords for each account.
Step 8: If your web browser has been affected by the malware, clear its cache and data:
- Open the “Settings” app.
- Scroll down and select the browser (e.g., Safari).
- Tap “Clear History and Website Data.”
- Confirm the action.
Step 9: Resetting network settings can help eliminate any network-related issues caused by malware:
- Open the “Settings” app.
- Scroll down and select “General.”
- Scroll to the bottom and tap “Reset.”
- Tap “Reset Network Settings” and confirm.
Step 10: If all else fails and the malware persists, you may need to perform a factory reset on your iPhone. This will erase all data on your device, so ensure you have a recent backup before proceeding:
- Open the “Settings” app.
- Scroll down and select “General.”
- Scroll to the bottom and tap “Reset.”
- Tap “Erase All Content and Settings” and confirm.
Step 11: After performing a factory reset, you can restore your iPhone from a backup:
- Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your iPhone until you reach the “Apps & Data” screen.
- Select “Restore from iCloud Backup” or “Restore from iTunes Backup,” depending on your backup method.
- Sign in to your Apple ID and choose the most relevant backup to restore your data.
How to Protect Yourself against Trojan Viruses
Trojan viruses are a prevalent form of malware that can compromise your device and data security. To protect yourself against Trojan viruses and other types of malware, it’s crucial to implement comprehensive security practices.
Following are some important measures you can take to safeguard your devices and personal information from Trojan infections:
1. Keep Your Operating System Updated
Regularly updating your device’s operating system is vital for security. Operating system updates, such as iOS for iPhones, Android for Android devices, or Windows for PCs, often include patches that address known vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by Trojans and other malware to gain access to your device or data. By keeping your operating system up to date, you ensure that you have the latest security protections.
2. Use Reputable Security Software
Installing and consistently updating reputable antivirus and anti-malware software on your devices is essential. These security programs actively scan your device for Trojans and other malicious software, helping detect and remove threats.
Regular updates to your security software ensure it has the latest threat definitions and detection capabilities to keep your device safe.
3. Use a VPN
Installing a VPN in your iPhone is another layer of protection for your online activities. A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a secure server, making it challenging for cybercriminals and malicious actors to intercept or monitor your data. It helps protect your privacy and adds an extra level of security when browsing the internet, especially on unsecured or public Wi-Fi networks.
While a VPN doesn’t directly protect against Trojans or malware, it safeguards your data during transmission and shields your IP address, making it more difficult for potential threats to target you.
4. Enable Automatic Updates
Enabling automatic updates for all your software, including your operating system, web browsers, and applications, is a crucial part of maintaining security. Many Trojans exploit vulnerabilities in outdated software.
By automating updates, you ensure that you receive the latest security patches promptly, reducing the risk of exploitation.
5. Download Apps Only from App Store
Limit app installations to trusted sources like the Apple App Store for iPhones or the Google Play Store for Android devices. These platforms have rigorous security measures in place to minimize the risk of malicious apps. Apps from unofficial sources may not undergo the same level of scrutiny, making them more susceptible to containing Trojans or malware.
6. Read App Permissions Carefully
When installing apps, carefully review the permissions they request. Be cautious if an app asks for unnecessary or intrusive permissions. For example, a simple game should not need access to your contacts or location. Deny permissions that seem unrelated to the app’s primary function.
7. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Creating strong, unique passwords for each of your online accounts is crucial. A strong password typically includes a combination of upper and lower-case letters, numbers, and special characters.
Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or common phrases. Consider using a reputable password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords.
8. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Whenever possible, enable 2FA on your online accounts. This additional layer of security requires you to provide a one-time code or authentication token in addition to your password. Even if a Trojan captures your password, it won’t be able to access your account without the second authentication factor.
9. Exercise Caution with Emails:
Be cautious when opening email attachments and clicking on links, especially if the sender is unfamiliar or the message seems suspicious. Email attachments are a common vector for Trojans and malware. Avoid downloading files or clicking links from unknown or untrusted sources.
10. Beware of Phishing Attempts
Phishing emails and websites often impersonate legitimate entities to trick you into revealing sensitive information. Be skeptical of unsolicited emails requesting personal data, login credentials, or payment information. Verify the authenticity of emails and websites before taking any action.
11. Keep Personal Information Secure:
Limit the sharing of sensitive information online, and only provide it when absolutely necessary. Even seemingly harmless data can be used in identity theft or targeted attacks. Be cautious about what you share on social media and in online forms.
12. Use a Firewall
Enable a firewall on your device to block unauthorized network access and incoming connections. Firewalls act as a barrier between your device and potential threats, preventing malicious entities from gaining access to your system or data. Most modern operating systems come with built-in firewall features that you can configure for enhanced security.
Enable a firewall on your device to block unauthorized network access and incoming connections. Most modern operating systems have built-in firewalls.
Examples of Trojan Viruses
The following are some examples that showcase the diversity and persistence of Trojan viruses in cybersecurity:
1. Zeus Trojan
The Zeus Trojan, also known as Zbot, is a notorious and enduring member of the Trojan virus family. First identified in 2007, it primarily targets Windows-based systems but has also been adapted to infect other platforms, including mobile devices.
Zeus gained infamy for its specialization in financial theft, mainly focusing on online banking and financial institutions. It employs various malicious techniques, such as keylogging, form grabbing, and remote control, allowing cybercriminals to steal login credentials, account information, and transaction data.
Often distributed through phishing emails and drive-by downloads, Zeus continually evolves with various variants and configurations tailored for specific targets. Infected machines can be harnessed together to form a botnet, which cybercriminals can remotely control for various purposes, including launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
2. Rakhni Trojan
The Rakhni Trojan is a versatile and adaptable member of the Trojan family, known for its capability to deliver different payloads, including ransomware. This multifunctional Trojan can perform various tasks depending on the cybercriminal’s objectives.
One of its notable features is its ability to deliver ransomware to infected systems, encrypting files, and demanding a ransom from victims. Some variants of Rakhni exhibit worm-like behavior, enabling them to spread to other connected devices through removable media, such as USB drives.
This characteristic makes Rakhni particularly concerned in environments with multiple interconnected systems. Rakhni’s payload flexibility allows cybercriminals to use it for various cyberattacks, making it a versatile and adaptable threat. Distribution typically occurs through phishing emails, malicious attachments, or compromised websites.
3. ILOVEYOU
The ILOVEYOU virus, while not a traditional Trojan, is a historic example of a computer virus that spread rapidly and caused significant damage.
It emerged in May 2000 as an email attachment with the subject line “ILOVEYOU” and a VBScript file attachment. When opened, it unleashed a destructive payload that overwrote files and spread to the victim’s Outlook address book, forwarding itself to contacts.
While not a Trojan in the traditional sense, the ILOVEYOU virus highlighted the potential for malware to exploit social engineering tactics to deceive users into executing malicious code. It caused widespread disruption and financial losses, emphasizing the importance of user awareness and cybersecurity practices.
Can iPhones get viruses from Safari?
iPhones have a lower risk of traditional viruses due to Apple’s stringent control over the iOS ecosystem. However, iPhones can still be vulnerable to other threats while using Safari. These threats include encountering malicious websites, falling victim to phishing scams, browser-based attacks exploiting vulnerabilities, and the potential for downloading malicious files or apps outside of the App Store.
FAQs
Yes, Trojan viruses can be removed from a device. To do so, you typically need to use antivirus or anti-malware software to scan your system, detect the Trojan, and remove it.
Yes, Trojans are a serious form of malware. They can perform various malicious actions on a compromised device, such as stealing data, controlling the device remotely, or delivering other malware.
Trojan virus warnings can be legitimate or part of a scam. Legitimate warnings typically come from reputable antivirus software when it detects a Trojan.
No, Trojan viruses are real and malicious as they are a type of malware designed to appear harmless but carry out harmful activities once they infect a device.
Yes, some Trojans are capable of spying on a device’s user. They can record keystrokes, capture screenshots, access files, and even activate a device’s camera or microphone to monitor and record user activities.
Yes, a Trojan virus on a phone can be very harmful. It can lead to data theft, unauthorized access, financial losses, and privacy breaches.
Yes, some Trojans are designed to steal passwords and other sensitive information. They can intercept keystrokes, capture login credentials, and access stored passwords on a compromised device.



No comments were posted yet