How To Protect Yourself Against Wi-Fi Pineapple Attacks

Bisma Farrukh

HAK5 developed the Wi-Fi Pineapple, which is a private company. Now you may be wondering, how do fruit and WiFi go hand in hand? Well, there’s a story behind its name. The WiFi Pineapple gets its name from its appearance. It’s a small, black device with multiple antennas at the top that stem outwards in different directions. These antennas look like a fresh pineapple’s top. Developers thought it looked like a tropical fruit, so it ended up with this name.
The WiFi Pineapple was created for a good cause: to run penetration tests. Penetration tests enable ethical hackers to uncover security vulnerabilities that malicious actors can potentially exploit in a company’s network or infrastructure that can be used against them. IT professionals and developers can then fix those vulnerabilities before they get exploited by hackers and cybercriminals. ure. Organizations often hire these pen testers to attack their network to expose any vulnerabilities.
However, sometimes, unfortunately, cybercriminals have started using WiFi pineapple to carry out cyberattacks. Although initially designed to offer protection against cyberattacks, it’s now begun to be used to inflict man-in-the-middle attacks. In this guide, we’ll explore how these WiFi Pineapple Attacks work and what steps you can take to ensure your network is safe and secure against these attacks. So, without further ado, let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What’s a Wi-Fi Pineapple And Their Uses?
A Wi-Fi Pineapple is a wireless penetration testing tool primarily designed for ethical hacking and security testing. It is developed and sold by HAK5, a private company specializing in creating penetration testing equipment.
The WiFi Pineapple is a rouge wireless access point that enables security professionals to simulate wireless attacks to determine the vulnerabilities of WiFi networks. The device has several use cases, some for a good cause and others for malicious purposes, which include:
- Man In The Middle Attacks: The Wi-Fi pineapple can intercept and inspect network traffic between devices and the internet. This allows cybersecurity experts to analyze communication patterns and identify potential security weaknesses using Man In The Middle Attacks.
- Wireless Security Auditing: Security professionals use the WiFi Pineapple to test the security of wireless networks by imitating and simulating common cyber attacks. This helps them identify and address any security vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them.
- DNS Spoofing: Wi-Fi Pineapple can manipulate DNS (Domain Name System) responses to redirect users to malicious and sketchy websites. This attack is also used for phishing attacks, where users are tricked into providing sensitive and confidential information.
- Credential Harvesting: By impersonating a legitimate WiFi network, the WiFi Pineapple can trick users into connecting to it. Once connected, it can steal sensitive information, login credentials, and other personal data transmitted over the network.
- Evil Twin Attacks: The device can create a malicious duplicate of a legitimate WiFi network, known as an “evil twin.” Users sometimes unknowingly connect to the rogue network, which enables attacks to monitor and track their activities.
How Does The Wi-Fi Pineapple Work?
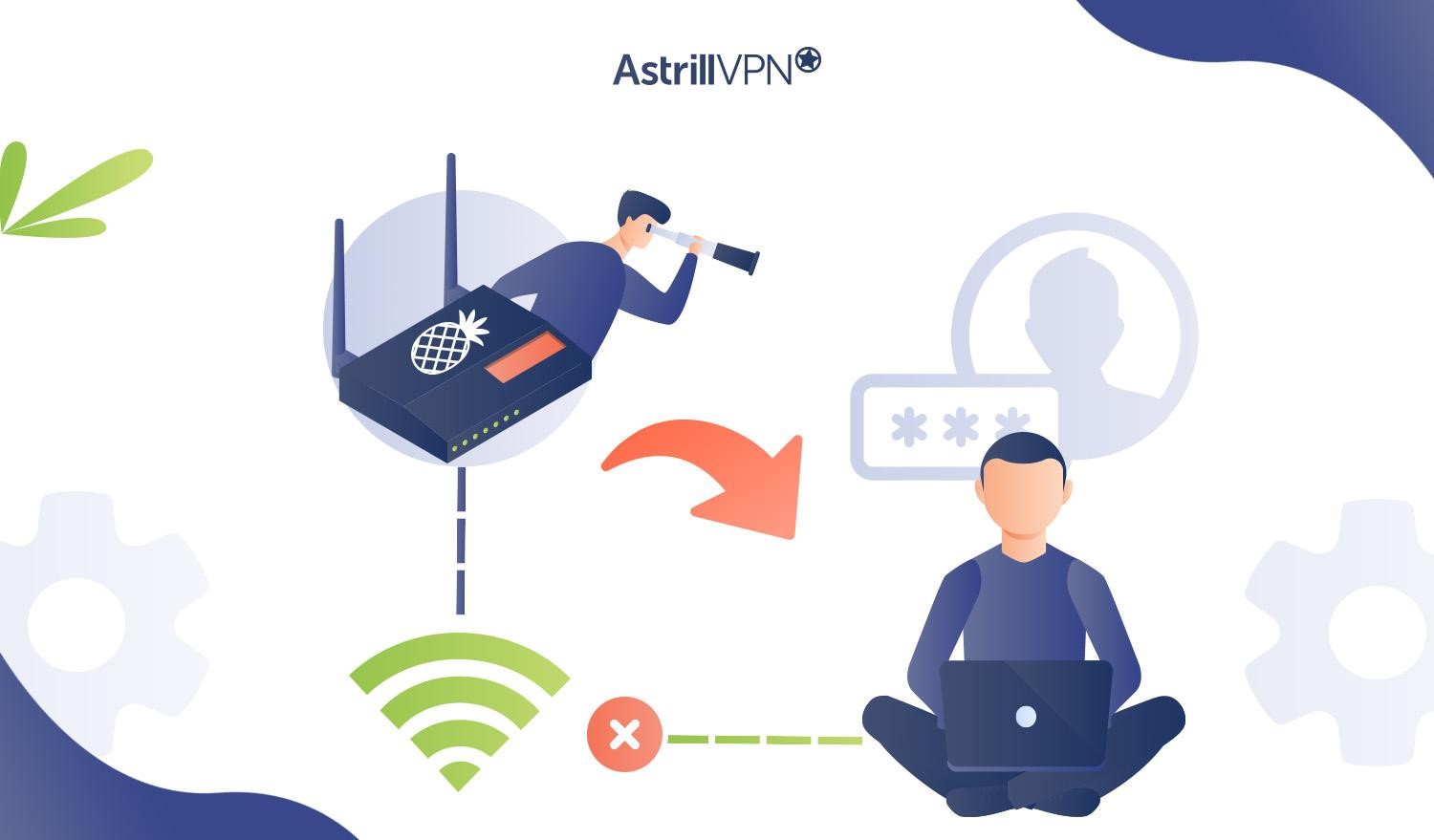
WiFi Pineapple is a tool for ethical hacking and should ideally only be used in scenarios where security testing has been authorized. Security professionals and penetration testers use these tools responsibly to identify and address network vulnerabilities. Here’s a detailed explanation of how the WiFi Pineapple works:
- The WiFi Pineapple works as a rogue access point. It creates a wireless network with a familiar SSID (Service Set Identifier) or network that devices may have previously connected to.
- The device monitors the airwaves for WiFi traffic and collects information about nearby WiFi networks.
- Devices sometimes send probe requests, looking for networks they’ve connected to. These requests also include the SSIDs of previously accessed networks.
- When the WiFi Pineapple detects a probe request for a network configured to impersonate, it gives a fake response, claiming to be the real network.
- When they receive responses from legitimate networks, devices can automatically connect without further user interaction. Devices automatically connect to networks they’re familiar with.
- As mentioned above, the WiFi Pineapple can create an evil twin by impersonating the characteristics of a legitimate WiFi network. Users can unknowingly connect to this route network, thinking it’s legitimate.
- Security professionals work to analyze the intercepted traffic to identify any security vulnerabilities, like unencrypted data, potential points of exploitation, and insecure protocols.
- The WiFi Pineapple can also log information about connected devices, captured data, and other activities on their network. Security professionals use this information to assess the network’s security and recommend improvements.
What Are Wi-Fi Pineapple Attacks?
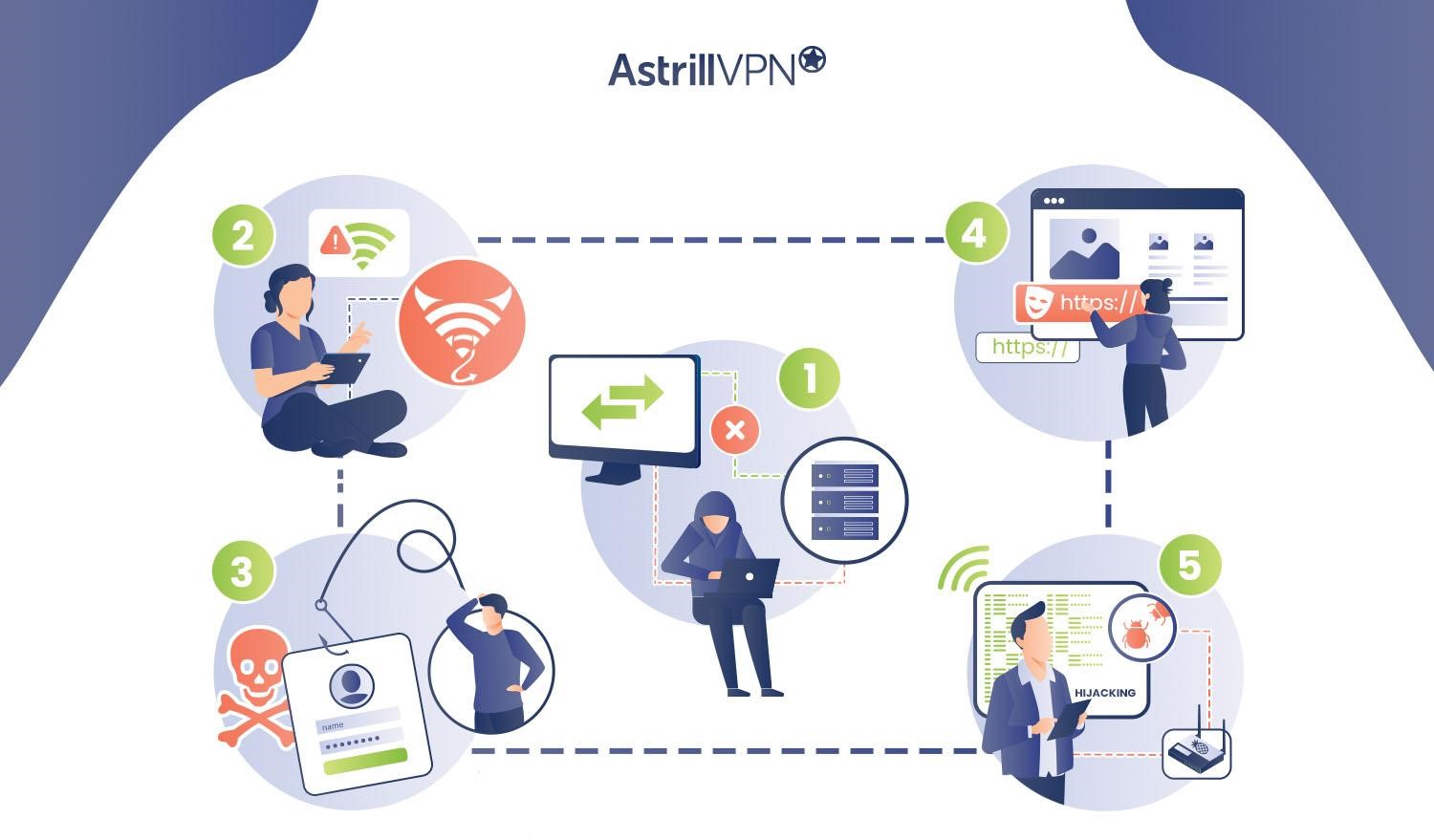
Now you know what the purpose of a WiFi Pineapple is, you can begin to understand what pineapple attacks are precisely. While WiFi Pineapples were created for a good cause, there’s a dark side. It also enables hackers and malicious actors to target vulnerable devices and steal sensitive and confidential data. When a hacker uses a WiFi Pineapple to gain unauthorized access to someone else’s network, this is known as a WiFi Pineapple attack.
Once the malicious actors gain unauthorized access to your network, these criminals can steal passwords, sensitive information like your financial details, and any other confidential data transmitted between your device and the internet. Once on the Rogue Access Point, the hackers can redirect users to a fake website or server they control. Here are some of the most common WiFi Pineapple Attacks, some of which we’ve already mentioned:
1) Man In The Middle Attacks
Using the WiFi Pineapple device enables cybercriminals to create a fake access point to execute Man In The Middle Attacks. They trick the user into connecting to the internet using a fake wireless network they control. In the attack, the hackers sneakily relay traffic between the victim’s device and the internet, stealing sensitive and confidential information such as banking details, login credentials, etc.
2) Evil Twin Attack
In an Evil Twin attack, the Wi-Fi Pineapple creates a rogue access point that imitates a legitimate WiFi network. When the devices in its vicinity decide to connect, they unknowingly connect to the “evil twin” network instead.
3) Credential Phishing
WiFi Pineapple can create phishing websites that impersonate legitimate websites, like e-commerce platforms or banking websites. When unaware users aim to connect to the fake network and attempt to gain access to these websites, they are redirected to the phishing site, where they enter their login details and payment information.
4) Fake HTTPS
Secure websites often use the HTTPS protocol to encrypt data and protect the users accessing the websites. In a fake HTTPS exploit, the hacker sits between the user and the website using the WiFi Pineapple. When a user requests a website (where most do not add HTTPS), the user connects to the less secure HTTP connection to the hacker. The attacker then connects the user to the less secure version of the website. This allows the hacker to intercept sensitive information.
5) Session Hijacking
Session hijacking attack involves intercepting and rerouting internet traffic, allowing the attackers to take over existing connections. When they capture the initial authentication process, attackers can impersonate the user and gain access to their online accounts and devices.
What Can A Hacker Achieve Through Wi-Fi Pineapple Attacks?
Once the hacker gains unauthorized access to your network through the WiFi Pineapple device, here are some of the ways they can cause users harm and compromise their confidential data:
- The hacker can steal confidential and sensitive data such as login credentials, credit card details, and other personal documents.
- The hacker can use the victim’s bandwidth and resources to their advantage by downloading files and doing activities that can potentially impact the performance of the victim’s devices.
Some Popular Wi-Fi Pineapple Attacks
1) 2018 Wi-Fi Pineapple Attacks at DEF CON
At the 2018 DEF CON security conference in Las Vegas, security researchers showed how WiFi Pineapples could be used to carry out large-scale phishing campaigns. The criminals set up a fake network called “DEF CON Free Wi-Fi” and captured the credentials of over 100 people attending the conference.
2) U.S. Financial Services Company Targeted By Hackers Using The Wi-Fi Pineapple
In 2022, unknown malicious actors spent $15000 to implement a cyberattack using WiFi Pineapple and other pentest tools using two DJI drones. The attack was conducted against an East Coast financial services company specializing in private investments. It was detected when the company noticed unusual activity in one of the collaboration tools used by teams across the company.
Linares reported this to the Register, saying that although he wasn’t a part of the incident response, he spoke to someone who was, and they said that the team discovered two DJI drones on the roof of the building. The team deployed embedded WiFi signal tracing and a Fluke system to identify the WiFi device. This took the team to the roof, where a “Modified DJI Matrice 600” and a “Modified DJI Phantom” were found. The Phantom happened to be carrying a “Modified WiFi Pineapple” device.
The hackers aimed to search the Confluence in hopes of finding credentials that could lead them to other internal company resources. The DJI Phantom was initially used for surveillance, where it successfully intercepted the employee’s credentials and WiFi days before the hacking attempt. The hackers hardcoded this into the pen testing tools deployed on the drone.
How Can I Protect My Network Against Wi-Fi Pineapple Attacks?

Now that you know the motive behind WiFi pineapple attacks and how hackers can use it to intercept your sensitive data, you can protect your network against them in several ways. Here are some of the most effective methods to help you avoid WiFi pineapple attacks in the future:
1) Use AstrillVPN
The first step to prevent yourself from being a victim of WiFi Pineapple attacks is to invest in a reliable VPN. AstrillVPN is your trusted VPN provider, which can help you protect against WiFi Pineapple Attacks. The VPN encrypts your data before sending it to its destination, so even if you’re connected to Pineapple, Pineapple would not be able to read the data that’s being transmitted since the VPN encrypts it. AstrillVPN will protect your internet traffic so no hacker or cybercriminal can gain unauthorized access to your network.
AstrillVPN also packs a punch with its top-notch security features, robust security protocols like OpenVPN and Wireguard, Split Tunneling and Kill Switch features, and a strict No-Logs Policy. Your data would be safe and secure and away from prying eyes. When installing a VPN for your company, ensure it has multi-factor authentication so employees can connect to the network securely. AstrillVPN helps you meet all of these needs. Here’s how you can install it and get started:
- Download and install AstrillVPN directly from the website.
- Log In with your credentials or create a new AstrillVPN account by registering.
- Choose a server location that works for you. You can also choose a Protocol that meets your needs and preferences.
- Turn on the VPN connection, and you’re all good to go.
Stay Safe on Public Wi-Fi – Try AstrillVPN
2) Beware Of Public Networks
Public networks are the most susceptible to cyberattacks. If you’re using the WiFi in a cafe, airport, or shopping mall, be sure to use a VPN so that your sensitive and confidential data gets encrypted and isn’t intercepted by malicious actors. But be cautious when connecting to a public network, as it is easy for the Pineapple to spoof their SSID. The easier it is to connect to a network, the easier it is for a Pineapple to spoof it.
3) Use Strong Passwords
Use a strong password for your devices and WiFi network for enhanced cybersecurity. Ensure that all of the organization’s employees follow the strong password rules, which include uppercase and lowercase letters, special characters, and numbers.
4) Install Anti-Malware Protection
Ensure your devices have reliable anti-malware software or Anti-virus software installed. These will help safeguard your device from online threats like phishing scams and malicious and sketchy websites. A reliable anti-malware/anti-virus software will have the following features:
- They offer real-time protection to detect and block malware.
- They use behavioral analysis to detect and block suspicious activities that indicate malware on your device.
- They include a firewall to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic, which helps prevent unauthorized access to your system.
- It identifies and blocks phishing attempts, protecting users from fake websites and scams designed to steal sensitive information.
- It keeps detailed logs of security events and provides reports on the software’s activities.
5) Use Websites With HTTPS Encryption
Many websites use HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure), which is encrypted to protect users visiting them. An HTTPS-encrypted website has a lock icon on the left side next to the URL. Also, ensure that your WiFi is secured with WPA3 encryption. It is the latest and most secure encryption protocol for WiFi networks.
Wrapping Up
The WiFi Pineapple is a wireless auditing platform enabling network security managers to conduct penetration testing. Penetration tests are considered ethical hacking, allowing organizations to look for security flaws in the network that a malicious actor can potentially exploit. And while it all started for a good cause, some hackers can exploit this and trick users into connecting to the WiFi network, thinking it is legitimate.
Pineapples have become convenient for hackers for several reasons: they have a long range, which allows the hacker to project their false network over a large region; they are affordable and contain tools to crack passwords and collect data. Luckily, this guide offers the most effective tips and tricks to tackle WiFi Pineapple attacks so that you don’t ever fall victim to it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
In the WiFi hijacking session, the WiFi Pineapple projects a fake WiFi network over a large area, where some users connect to the wrong network. Then, this enables the attacker to harvest their data.
The WiFi Pineapple has a default IP address of 172.16. 42.1 and assigns clients with an IP address in the range of 172.16. 42.100-150 through its onboard DHCP server.
Aside from your computer’s IP address, a separate IP address is assigned to your wireless router. When you’re setting up WiFi internet access on another device or troubleshooting a WiFi connection, you will need to know your computer’s or router’s IP address.
If you’re using some of the WiFi pineapple features incorrectly, that could be considered illegal. One of these features includes its ability to spoof WiFi networks, deceiving users into connecting to the Pineapple WiFi network, thinking it’s legitimate.
The WiFi Pineapple MKV wasn’t designed to be used as a router. It could be used as one; however, you should avoid running the WiFi pineapple firmware on it.
The diversion of HAK5 products and technology contrary to U.S. law is prohibited. Depending on your residence, additional import or export requirements can apply.


No comments were posted yet