What is Identity Theft, and How to Prevent It?

Arsalan Rathore

Identity theft, a pervasive and disruptive cybercrime, poses a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and institutions. Cybercrime and identity theft trends are growing because technology is advancing rapidly, but people aren’t taking steps to protect what matters.
Every individual must understand Identity theft, its dangers, and how everyone can prevent it. In this guide, we have discussed everything in detail to make you more aware of the things related to identity theft so that you can take the necessary steps for your safety.
Table of Contents
What is Identity Theft?
Identity theft is a malicious act in which an individual or entity fraudulently acquires and uses someone else’s personal information, such as their name, Social Security number, financial account details, or other identifying information, without their consent. Identity theft typically involves engaging in various forms of fraudulent activity, including financial fraud, accessing medical services, committing crimes, and more.
Identity theft is financially damaging and can have severe emotional and psychological repercussions for the victims. After identity theft, it can take victims years to fully recover their financial and personal well-being.
7 types of identity thefts
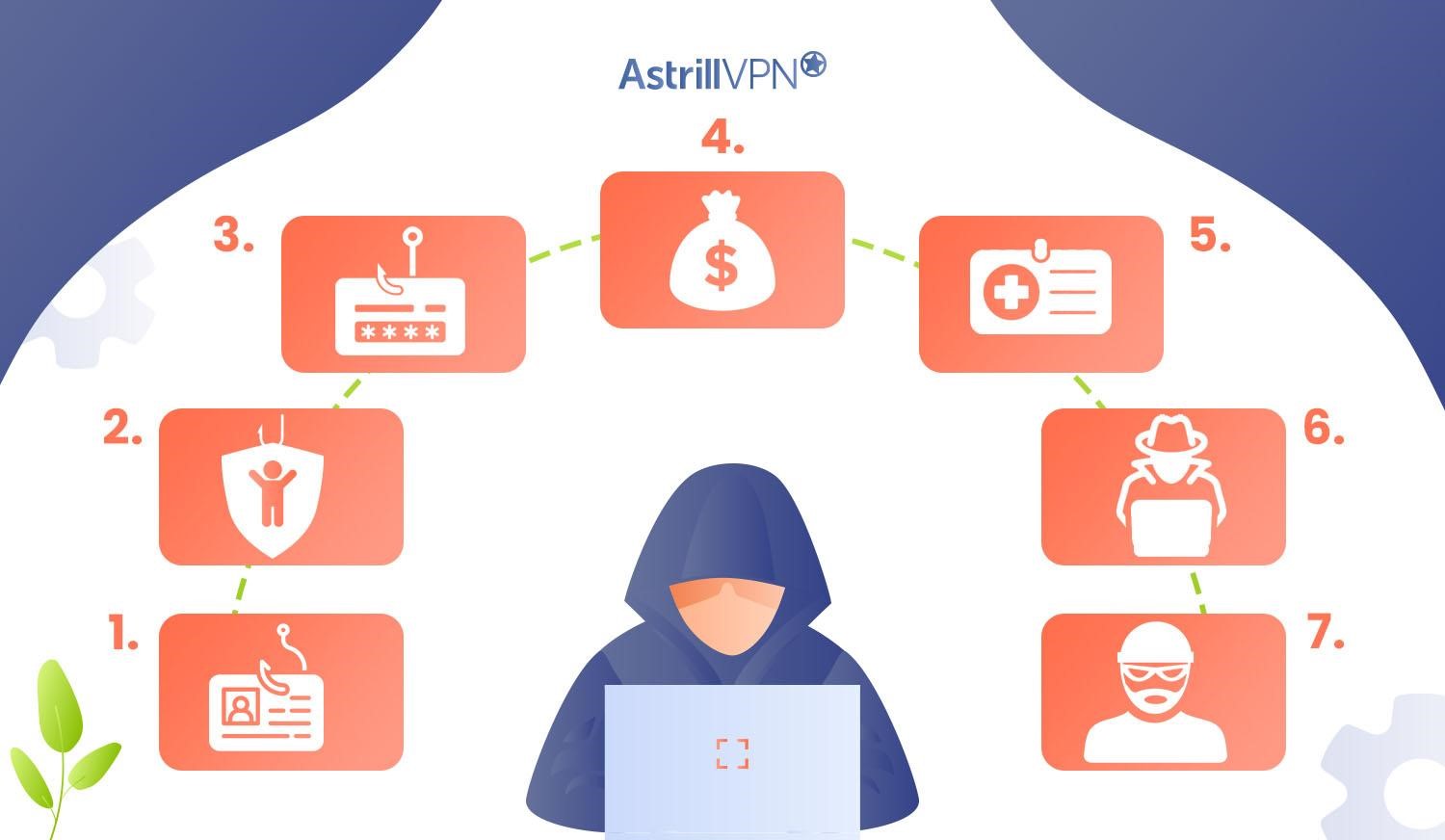
Identity theft is not a one-size-fits-all crime; it comes in various forms, each targeting specific aspects of an individual’s identity and life. Here are seven common types of identity theft:
1. Credit identity theft
Credit identity theft is one of the most prevalent forms of identity theft. In this type of identity theft, the perpetrator gains access to an individual’s personal information, such as their Social Security number and date of birth, to open new lines of credit or take over existing credit accounts. They then accumulate debt or make unauthorized transactions in the victim’s name, damaging their credit history and financial stability.
2. Child identity theft
This may seem strange, and you’d wonder what is child identity theft. Child identity theft occurs when a criminal uses a child’s personal information, often obtained from birth records, school forms, or medical records, to create fraudulent accounts or commit financial fraud. Because children typically don’t have a credit history, this identity theft can go undetected for years, making it even more challenging to resolve.
3. Synthetic identity theft
It involves creating a fictitious identity by combining real and fabricated personal information. The fraudster may use elements of a stolen Social Security number or other data to create a new identity, which they then use to open bank accounts, apply for loans, or engage in other fraudulent activities.
4. Taxpayer identity theft
Taxpayer identity theft occurs when someone uses another person’s Social Security number to file fraudulent tax returns and claim refunds. Victims often discover this type of identity theft when they attempt to file their tax return and find that an imposter has already filed it.
5. Medical identity theft
This theft involves stealing an individual’s personal information, such as their health insurance details or Social Security number, to obtain medical services, prescription drugs, or even surgery in the victim’s name. This can lead to inaccurate medical records and potential health risks for the victim.
6. Account takeover
Account takeover is a form of digital identity theft. It occurs when a fraudster gains unauthorized access to an individual’s online accounts, such as email, social media, or financial accounts, by stealing/hacking login credentials. They may use these compromised accounts to steal money and personal information or spread malicious content.
7. Criminal identity theft
Criminal identity theft occurs when someone uses another person’s identity when arrested or cited for a crime. This can result in the victim having a criminal record, facing legal consequences, or experiencing difficulties with background checks and employment opportunities.
11 Signs of Identity Theft
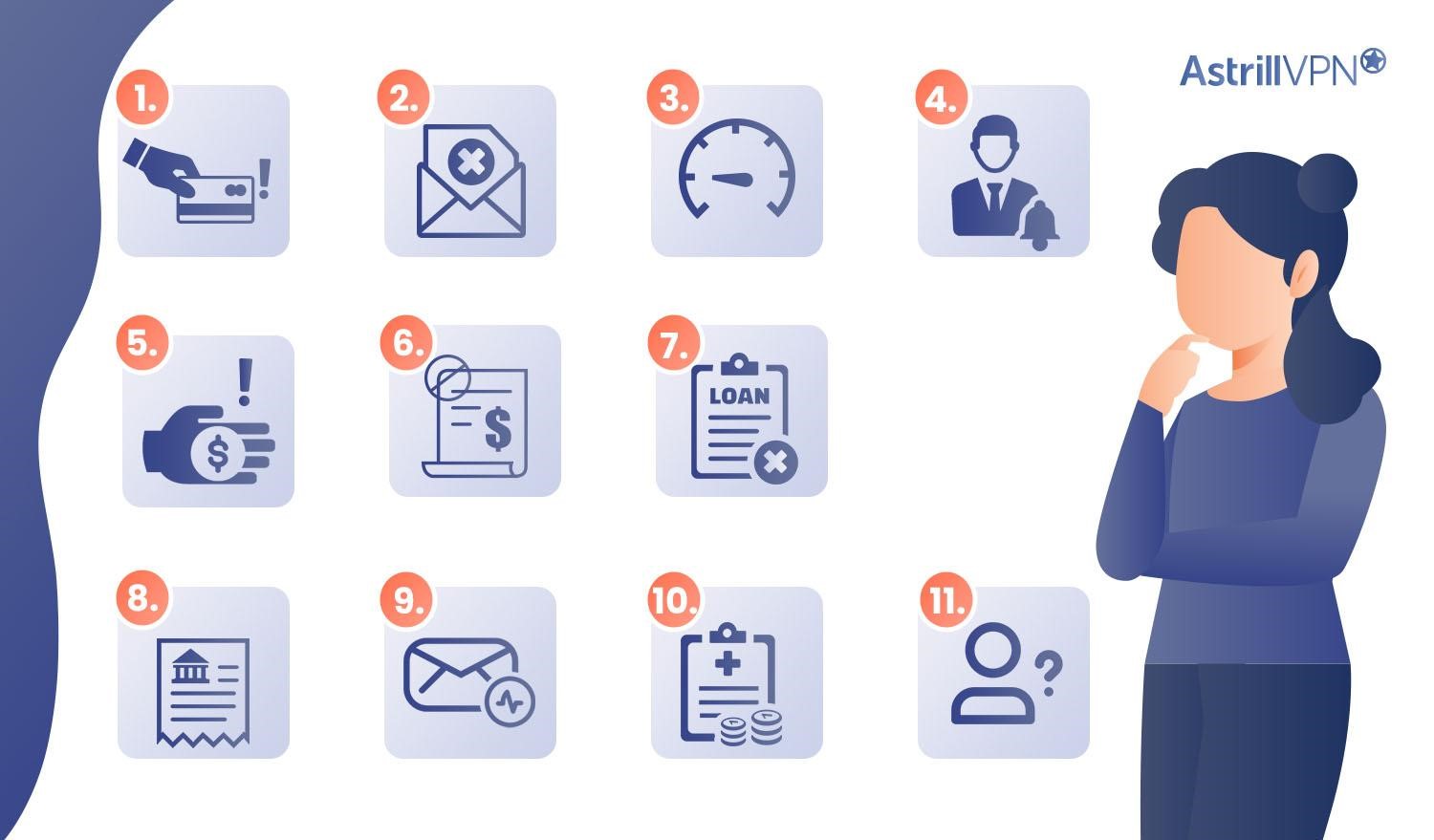
Identity theft can have severe consequences, and recognizing the signs is crucial for early detection and mitigation. Here are 11 specific indicators that you may be a victim of identity theft,
1. Unfamiliar or Unauthorized Transactions
Regularly review your bank and credit card statements for any transactions you didn’t initiate or don’t recognize. These transactions may include purchases, withdrawals, or transfers. If you spot any unauthorized activity, contact your financial institution immediately to investigate and report the issue.
2. Missing Mail or Statements
Suppose you suddenly stop receiving important mail, such as bills, bank statements, or other financial statements. In that case, it may indicate that someone has fraudulently changed your mailing address to intercept sensitive information.
3. Sudden Drops in Credit Score
Monitor your credit score regularly, and be alert to significant and unexplained drops. Identity thieves often use your personal information to open fraudulent credit accounts or engage in financial activities that can negatively impact your credit history. Check your credit reports for any unauthorized changes or accounts.
4. Notification of New Accounts
Receiving notifications, statements, or account-related correspondence for accounts you didn’t open is a clear sign of social media identity theft. These accounts may include credit cards, loans, or utility services.
5. Collection Notices for Unknown Debts
Collection notices or calls regarding debts you don’t recognize may indicate that an identity thief has incurred debts in your name. Request validation of the debt in writing and dispute any fraudulent claims with the collection agency.
6. Tax-Related Issues
Tax-related identity theft can involve fraudulent tax returns filed under your name. If you receive notices from the IRS about multiple returns or tax obligations for income you didn’t earn, contact the IRS immediately to rectify the situation. You may need to file an identity theft affidavit and a corrected tax return.
7. Rejection of Credit or Loans
Unexpected denials for credit applications or loans can be due to fraudulent activity affecting your credit report.
8. Unexpected Account Statements
Receiving account statements for financial or credit accounts you didn’t open indicates identity theft. Contact the financial institution or creditor to report the fraudulent accounts, close them, and request an investigation.
9. Unusual Email or Account Activity
Be cautious of suspicious emails, password reset requests, or unrecognized login attempts on your online accounts. Identity thieves may try to gain unauthorized access to your accounts.
10. Medical Billing Issues
Unexpected medical bills or insurance claims for services you didn’t receive can signal medical identity theft.
11. Unfamiliar Accounts on Your Online Profile
Regularly review your online profiles, such as social media or email accounts, for unfamiliar or unauthorized connections, messages, or posts. Identity thieves may use your accounts for malicious purposes.
11 Simple and Smart Ways to Prevent Identity Theft
Identity theft prevention is essential for safeguarding your personal and financial information. Here are 11 effective strategies to help protect yourself from identity theft:
1. Freeze Your Credit
Consider placing a security freeze on your credit reports with all three major credit bureaus (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion). This action restricts access to your credit information, making it easier for identity thieves to open new credit accounts in your name with your permission. When you need to apply for credit, you can temporarily lift the freeze with a unique PIN.
2. Protect your Social Security Number
Your Social Security number (SSN) is a prime target for identity theft. Keep your SSN confidential, and avoid carrying your Social Security card in your wallet. Only provide it when necessary, and verify the legitimacy of requests for your SSN, primarily online.
3. Prevent Phishing and Spoofing
Phishing attacks involve deceptive emails, websites, or messages that impersonate trusted entities to trick you into revealing sensitive information. Avoid unsolicited emails, especially those requesting personal information or urgent action. Verify sender legitimacy and web addresses before clicking links or sharing sensitive data.
4. Use Strong Passwords
Create strong, unique passwords for your online accounts, incorporating a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Consider using a reputable password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords.
Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible to require an additional verification step, such as a code sent to your phone, for enhanced security.
5. Turn On Alerts
Set up account alerts for your financial, credit card, and bank accounts. These alerts can notify you via email, text message, or app notification of unusual account activity, significant transactions, or changes to your personal information. Promptly addressing suspicious activity is crucial to limiting potential damage.
6. Protect Your Mail
Secure your mailbox to prevent mail theft. Use a locked mailbox or rent a secure PO box to receive important mail. Shred documents with personal information before disposal, including bills, bank statements, and credit card offers, to deter dumpster diving by identity thieves.
7. Use a VPN
When accessing the internet, use a reliable VPN like AstrillVPN to encrypt your online activity and protect your data from potential eavesdropping on public Wi-Fi networks. Astrill VPN enhances online privacy and security by routing internet traffic through a secure server.
8. Use a Digital Wallet
Digital wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay provide secure payment methods that don’t require sharing your actual credit card details with merchants. Instead, they use tokenization to protect your financial information during transactions. Utilize digital wallets whenever possible for safer online and in-store payments.
9. Protect Your Mobile Devices
Secure your mobile devices with strong, unique passcodes, PINs, or biometric authentication methods like fingerprint or facial recognition. Install reputable security apps to guard against malware and regularly update your device’s operating system and apps to ensure you have the latest security patches.
10. Check Your Credit Reports Regularly
Under federal law, you’re entitled to one free credit report per year from each of the three major credit bureaus. Take advantage of this by regularly checking your credit reports for discrepancies, unauthorized accounts, or suspicious activity. Reviewing your credit reports helps you detect and address identity theft promptly.
11. Monitor Financial and Medical Statements
frequently monitor your financial account statements for any unusual or unauthorized transactions. Review your credit card, bank, and investment account statements diligently. Additionally, keep a close eye on your medical statements to detect fraudulent medical billing or services you still need to receive.
Promptly report discrepancies or unauthorized charges to the respective institutions and dispute them if necessary.
How does Identity Theft Happen Online?
Understanding the various methods of identity theft is crucial for taking proactive steps to protect yourself. Following are the 13 ways through which identity theft occurs:
1. Lost wallet
A lost or stolen wallet is one of the simplest yet effective methods for identity theft. When an individual loses their wallet, it often contains a treasure trove of personal information, including driver’s licenses, credit cards, and sometimes Social Security cards.
A thief who gains access to such a wallet can use the contents to impersonate the victim, make unauthorized purchases, or commit fraud. To mitigate this risk, individuals should minimize the personal information they carry in their wallets, avoid storing sensitive documents like Social Security cards, and promptly report any lost or stolen wallets to the relevant authorities and institutions.
2. Mail theft
Mail theft is a method favored by identity thieves because it grants them access to a wide range of sensitive information. Thieves can intercept bills, bank statements, tax documents, and credit card offers from victims’ mailboxes. With this information, they can open fraudulent accounts or commit financial fraud.
3. Using public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi networks at cafes, airports, and hotels are convenient but can pose significant security risks. Identity thieves can intercept data transmitted over unsecured public networks, potentially gaining access to usernames, passwords, and other sensitive information.
To safeguard against this threat, individuals should use a VPN to encrypt their internet connections when accessing public Wi-Fi. A VPN like AstrillVPN creates a secure tunnel that protects data from eavesdroppers, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential.
4. Data breaches
Data breaches occur when cybercriminals gain unauthorized access to databases containing vast amounts of personal and financial information. These breaches can affect individuals, businesses, or even government agencies. In the aftermath of a data breach, stolen data often ends up on the dark web, where identity thieves can buy and sell it.
5. SIM card swap
A SIM card swap involves an identity thief convincing a mobile carrier to transfer a victim’s phone number to a new SIM card, often without the victim’s knowledge. Once the thief controls the victim’s phone number, they can gain access to two-factor authentication codes and reset passwords for various accounts.
Protecting against SIM card swaps involves contacting your mobile carrier to establish security protocols, such as requiring in-person verification before making such changes.
6. Phishing or spoofing
Phishing and spoofing attacks are deceptive techniques identity thieves use to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information. Phishing emails or messages often mimic trusted entities, such as banks or government agencies, and encourage recipients to click on malicious links or provide personal information. Spoofing involves manipulating caller IDs or email addresses to appear legitimate.
7. Skimming
Skimming devices are physical tools placed on ATMs, gas pumps, or point-of-sale terminals to steal card information when individuals make legitimate transactions. These devices capture the data encoded on the magnetic stripe of credit or debit cards. Identity thieves then use this stolen data to create counterfeit cards or make unauthorized purchases.
8. Phone scams
Phone scams often involve impostors posing as legitimate entities, such as government agencies or tech support, to trick individuals into revealing personal information or making fraudulent payments. These scams can be convincing and intimidating.
9. Looking over your shoulder
Shoulder surfing is a low-tech but effective method of identity theft where an attacker observes a victim’s keystrokes or PIN entry while using an ATM, entering a password on a computer, or inputting sensitive information on a mobile device.
10. Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, includes viruses, Trojans, spyware, and other malicious programs that can infect computers and mobile devices. These programs can capture keystrokes, steal login credentials, and access personal information. Protecting against malware involves using reputable antivirus and anti-malware software, keeping operating systems and software up to date, and being cautious when downloading files or clicking links from untrusted sources.
11. Dumpster Diving
Dumpster diving is a physical method of identity theft where attackers sift through a victim’s discarded documents and trash to find personal information, such as bank statements, credit card offers, or tax documents.
12. Social Engineering
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into disclosing confidential information willingly. This technique often includes tactics like pretexting (creating a fabricated scenario), baiting (enticing victims with something enticing), or impersonating trusted authorities over the phone or in person.
13. Insider Threats
Insider threats occur when individuals with authorized access to sensitive data misuse that access for malicious purposes. This can include employees or contractors who abuse their privileges to steal or misuse personal information.
What is the most common identity theft?
The most common type of identity theft involves financial fraud, like unauthorized credit card charges or fraudulent tax filings using stolen personal information. Criminals can steal credit card details, Social Security numbers, or bank account information to make purchases, file fake tax returns, or open new accounts in someone else’s name.
How to report identity theft?
Discovering that you’ve fallen victim to identity theft can be distressing, but taking swift action is crucial. Here are some steps you should take to report identity theft:
- Start by filing a police report with your local law enforcement agency. Provide them with as much detail as possible about the identity theft, including any fraudulent transactions or activities.
- Visit the FTC’s official website (ftc.gov) or call their Identity Theft Hotline at 1-877-438-4338 (1-877-ID-THEFT) to report identity theft.
- Contact each of the three major credit bureaus—Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion—to place a fraud alert on your credit reports.
- Reach out to your banks, credit card companies, and any other financial institutions where you have accounts affected by identity theft.
- Continuously monitor your financial and credit accounts for any suspicious or unauthorized activity.
- Contact the respective financial institutions immediately if you discover any fraudulent accounts opened in your name. Request that they close these accounts and issue a letter confirming the fraudulent activity.
- Complete an Identity Theft Affidavit, available from the FTC, to officially report the identity theft to creditors and businesses.
- If the identity theft involves fraudulent tax returns or related issues, contact the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) at 1-800-908-4490 to report the incident and request guidance on resolving tax-related identity theft.
- If your Social Security number was misused for identity theft, contact the SSA and report the incident.
Government Agencies and Tools for Protecting Your Identity
To protect your identity, consider utilizing government agencies and tools:
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC): It provides valuable resources, including identity theft reporting tools, information on prevention, and steps for recovery. Their website (ftc.gov) and IdentityTheft.gov offer comprehensive guidance.
- AnnualCreditReport.com: It allows you to access one free credit report per year from each of the three major credit bureaus, aiding in the detection of unauthorized activity.
- The Social Security Administration (SSA) provides information on protecting your Social Security number and reporting any misuse or identity theft on its website (ssa.gov).
- The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) offers resources for addressing tax-related identity theft, including guidance on reporting and resolving it on its website (irs.gov).
- The U.S. Postal Inspection Service: It can assist if you suspect mail theft or fraudulent use of the mail in connection with identity theft.
What happens when you report identity theft?
First, you’ll file a report with your local police, and they’ll document the details. Then, if you contact the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) or use IdentityTheft.gov, they’ll create an Identity Theft Report to prove you’re a victim.
You should also alert the credit bureaus to place a fraud alert on your credit reports, making it harder for thieves to use your credit. You’ll need to monitor your accounts for suspicious activity, like strange purchases or new accounts in your name.
If you find any, you’ll work with your banks and credit card companies to secure your accounts. They may even close fraudulent accounts and give you proof of the fraud. If there’s tax-related fraud, you’ll report it to the IRS. Keep records of all your communications and documentation throughout the process.
The goal is to resolve identity theft, protect your accounts, and recover any losses. Remember to take steps to prevent future identity theft, like setting up credit freezes and using strong passwords to keep your information safe.
Online Identity Theft Examples and Statistics
In recent years, there has been a substantial increase in the number of identity theft cases reported to the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). According to the FTC’s Consumer Sentinel Network (CSN) report, the most notable surge occurred from 2019 to 2020, when the reported cases more than doubled.
This alarming statistic reflects the growing prevalence of identity theft, which deserves our attention. Several factors, including increased digitalization, pandemic-related scams, and data breaches, have contributed to this rise. Here’s an outlook of some alarming identity theft stats:
- According to Javelin Strategy, an estimated 15 million Americans had their identities stolen in 2021, revealing the widespread nature of this crime.
- Most identity theft cases in 2021 went unreported, as highlighted by Javelin Strategy & Research’s 2022 Identity Fraud Study.
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) received over 1.4 million reports of identity theft in the same year, underscoring the scale of this issue.
- Regarding financial impact, identity thieves stole approximately $52 billion from Americans the previous year, demonstrating the substantial economic consequences.
- More than 40 million U.S. consumers fell victim to identity theft in 2021, emphasizing the urgency of addressing this issue.
- The age group most vulnerable to identity theft in 2021 was individuals aged 30 to 39, as indicated by the FTC’s Consumer Sentinel Network Data Book for that year.
- According to the Federal Trade Commission, criminals exploited the COVID-19 pandemic to defraud taxpayers, resulting in over $750 million in theft through stimulus scams since January 2020.
FAQs
Yes, identity theft is a significant problem because it involves the unauthorized use of someone’s personal information for fraudulent activities, leading to financial losses and personal hardships for victims.
Theft involves taking someone’s property or possessions without permission. In contrast, identity theft is a specific form of theft where someone steals personal information, like Social Security numbers or credit card details, to impersonate the victim and commit fraudulent activities using their identity.
● Victims often incur financial losses due to unauthorized transactions, stolen funds, or fraudulent loans taken out in their name.
● Identity theft can harm a victim’s credit score and credit history, making it difficult to secure loans or credit in the future.
● Dealing with the aftermath of identity theft can be emotionally distressing, causing anxiety, frustration, and a sense of violation.
Yes, identity theft is a common cybercrime, affecting millions of individuals yearly. The rise of digital technology and online transactions has made it easier for criminals to commit identity theft, contributing to its prevalence.
Identity theft is a type of computer crime, but not all computer crimes are identity theft. Computer crimes include various illegal activities done online, like hacking or cyberbullying. On the other hand, identity theft is a specific kind of computer crime where personal info, like Social Security numbers, is stolen to commit fraud.

No comments were posted yet