What is FileRepMalware? A Complete Guide to Detection and Protection

Arsalan Rathore
FileRepMalware is a type of malware detected by antivirus programs under the “FileRep” classification. Its suspicious traits characterize it, and it may lack a known signature in malware databases. This classification aids in identifying new threats. FileRepMalware is often linked to files from unknown sources that resemble legitimate software, making detection difficult. Its impact can vary from minor issues to severe data breaches and system vulnerabilities.
In this guide, we’ll explore how FileRepMalware operates, how to detect it, and the steps to prevent it from infecting your devices.
Table of Contents
What is FileRepMalware ?
FileRepMalware is a classification used by antivirus programs to identify files that exhibit characteristics of malicious behavior but may not yet be recognized by traditional malware signature databases. The term “FileRep” refers to “file reputation,” a method employed by security software to assess the potential risk of files based on a combination of factors, including the file’s origin, behavior, and history.
When a file is downloaded or accessed on a device, antivirus programs evaluate it using various detection methods. A file may be flagged as FileRepMalware if it does not have a known signature in the antivirus provider’s database but displays unusual behavior that suggests it could be harmful. For instance, the file might try to modify system files, connect to remote servers, or exhibit other behaviors commonly associated with malware. In such cases, even without a specific signature to identify it, the file is still treated as a threat due to its suspicious nature.
How Antivirus Programs Identify FileRepMalware?
Antivirus programs use a combination of detection methods to identify and flag FileRepMalware. These methods include signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, behavior analysis, and file reputation.
1. Signature-Based Detection
Traditional antivirus software relies on a database of known malware signatures to identify threats. However, FileRepMalware is often flagged when it doesn’t match any known signatures. In this case, antivirus programs may rely on reputation-based scoring to determine whether the file is potentially dangerous.
2. Heuristic Analysis
Heuristic analysis involves examining files’ behavior to detect unusual or suspicious activity. Antivirus programs look for behaviors commonly associated with malware, such as attempts to alter system files, communicate with unknown remote servers, or run executable code without user consent. A file exhibiting these behaviors may be flagged as FileRepMalware, even if it doesn’t match a known malware signature.
3. Behavioral Detection
Some antivirus programs use behavioral detection techniques to identify malware after execution. This involves monitoring the activities of files during runtime to see if they engage in suspicious actions, such as modifying system settings or spreading to other devices. If such activities are detected, the file may be flagged as FileRepMalware, and further action may be taken to quarantine or remove it.
4. File Reputation and Cloud-Based Analysis
Modern antivirus programs often leverage cloud-based databases and real-time file reputation systems to assess the risk associated with a file. When a file is downloaded or executed, the antivirus software may check its reputation by querying a cloud database that aggregates data from other users and systems. If the file has been flagged as potentially dangerous by other users or by the antivirus vendor, it may be classified as FileRepMalware. This real-time data collection helps detect emerging threats before they are formally identified in signature databases.
5. Sandboxing
Some antivirus software employs sandboxing techniques, where suspicious files are run in an isolated environment to observe their behavior. If a file shows signs of malicious activity, such as attempting to install additional malware or stealing data, it is flagged as FileRepMalware and removed from the system.
How Does FileRepMalware Spread?
FileRepMalware, like many types of malware, spreads through various methods, often leveraging user actions or system vulnerabilities to propagate. Understanding how FileRepMalware spreads can help individuals and organizations implement better security measures to prevent infections. Some of the most common ways in which FileRepMalware spreads include:
1. Phishing Emails
Phishing emails are one of the most common distribution methods for FileRepMalware. Cybercriminals often disguise malicious attachments or links as legitimate messages, such as fake invoices, job offers, or security alerts. When a user opens the attachment or clicks on a link, it can trigger the download or execution of FileRepMalware, often without the user’s knowledge. These emails are often designed to create a sense of urgency, tricking recipients into acting quickly and bypassing security precautions.
2. Malicious Downloads
Another primary method for FileRepMalware distribution is downloading files from untrusted sources. This can include downloading software from unofficial websites, pirated content, or files shared via peer-to-peer (P2P) networks. Files disguised as legitimate programs (e.g., software updates, games, or multimedia files) may harbor FileRepMalware. Once downloaded and executed, the malware infects the system and can start spreading to other devices or files.
3. Software Vulnerabilities
Exploiting known software vulnerabilities is a common tactic for FileRepMalware to spread. Cybercriminals often target unpatched security flaws in popular software or operating systems, allowing them to install malware remotely without requiring any interaction from the user. These vulnerabilities can exist in browsers, media players, email clients, or even the operating system itself. Once the malware gains access, it may download additional payloads, spread through connected networks, or exploit the compromised system for further attacks.
4. Infected Websites and Drive-By Downloads
Another way FileRepMalware spreads is through compromised or malicious websites. Cybercriminals can inject malware into websites that users visit, either through malicious advertisements (malvertising) or by directly compromising the website’s code. Once a user visits the infected site, malware can be silently downloaded and executed without their knowledge. These “drive-by downloads” often occur without any visible sign to the user, making them particularly dangerous.
5. USB Drives and External Devices
FileRepMalware can also spread through infected USB drives or other external storage devices. When a user plugs in an infected USB stick or external hard drive into their computer, the malware may automatically execute or copy itself onto the system. This method is commonly used in environments where multiple devices are connected or in corporate settings where removable drives are frequently shared among users.
6. Network Propagation
Once an infected system, FileRepMalware may spread across a network, particularly in corporate or enterprise environments. This can occur through unsecured network shares, remote desktop services, or other network vulnerabilities. Once on a network, the malware can infect other systems, often exploiting weak security measures to propagate quickly across multiple devices.
How to Detect FileRepMalware?
Detecting FileRepMalware can be challenging, especially because it often disguises itself as a legitimate process or file. However, you can use several methods and tools to identify and confirm the presence of this type of malware on your system. Early detection is crucial to minimize the damage caused by FileRepMalware. Here are some key ways to detect an infection:
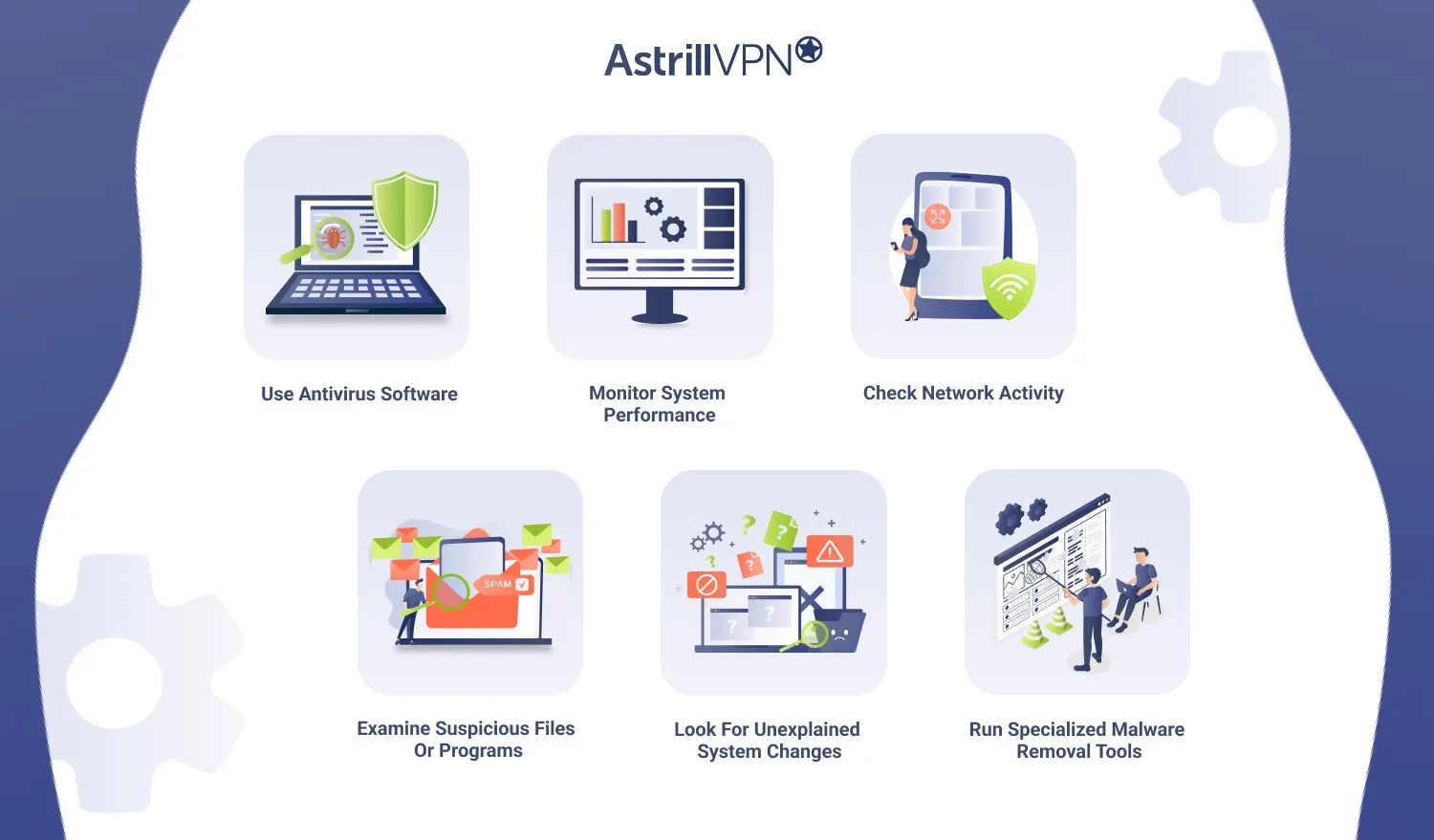
1. Use Antivirus Software
Most antivirus programs are designed to detect and quarantine malware, including FileRepMalware, through signature-based detection, heuristic analysis, and real-time scanning. These programs look for known malware signatures or suspicious behavior that matches the characteristics of FileRepMalware. Keeping your antivirus software updated ensures it can identify the latest threats, including evolving versions of FileRepMalware. Regularly run full system scans and enable real-time protection features.
2. Monitor System Performance
A noticeable slowdown in system performance can indicate that malware is running in the background. FileRepMalware often consumes significant system resources such as CPU and memory, leading to sluggishness or crashes. If you notice your system is abnormally slow or unresponsive, it could be a sign that malware is running. Open your Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac) and look for unfamiliar processes consuming excessive resources.
3. Check Network Activity
Malware often communicates with remote servers to receive commands or exfiltrate data. Unusual network traffic, such as high outbound data usage or connection attempts to suspicious IP addresses, can indicate malware activity. You can monitor your network activity using built-in operating system or third-party network monitoring tools. Use a firewall or network monitoring tool to detect suspicious connections and activity.
4. Examine Suspicious Files or Programs
FileRepMalware may install files or programs that seem out of place. These files can often be hidden or disguised under legitimate-sounding names. Investigate unfamiliar or unexpected files in your system directories, particularly in the startup folder or system directories. Use a file scanner tool to check suspicious files for malware. Pay close attention to files with unusual names or that were recently created.
5. Look for Unexplained System Changes
Malware often modifies system settings, such as changing your default browser, homepage, or search engine. If you notice that your browser’s settings have changed without your consent or you encounter new toolbars or add-ons, it could indicate malware infection. Regularly review your system and browser settings for any unauthorized changes.
6. Run Specialized Malware Removal Tools
Many security companies offer specialized malware removal tools that are designed to target and remove specific types of malware, including FileRepMalware. These tools can perform deep scans and identify infections that may be missed by standard antivirus programs. Use specialized malware removal tools such as Malwarebytes or HitmanPro to scan for and remove hidden malware.
Steps to Remove FileRepMalware
If you’ve detected FileRepMalware on your system, it’s essential to act swiftly to remove it and prevent further damage. The following steps outline how to remove FileRepMalware effectively:
1. Disconnect from the Internet
Before proceeding with malware removal, disconnect your device from the internet to prevent the malware from communicating with remote servers or spreading to other devices on the network. Turn off Wi-Fi or unplug your Ethernet cable to isolate the infected device.
2. Boot Into Safe Mode
Starting your computer in Safe Mode minimizes the chances of FileRepMalware being active. Safe Mode only loads essential system files, making identifying and removing malicious software easier. Once in Safe Mode, the malware’s processes will likely be inactive, allowing you to delete it more easily. To boot into Safe Mode, restart your computer and press the appropriate key (e.g., F8 or Shift + F8 for Windows or Command + R for macOS) to enter recovery options.
3. Run an Antivirus Scan
Once in Safe Mode, run a full system scan using your antivirus software. Make sure your antivirus database is up-to-date before scanning. The software should detect and quarantine the malicious files associated with FileRepMalware. Follow the on-screen instructions to remove any detected malware and restart your system after the scan.
4. Use Malware Removal Tools
In addition to antivirus software, you can use specialized malware removal tools to eliminate FileRepMalware. These tools can detect and remove hidden malware that may not be picked up by traditional antivirus solutions. Download and run tools like Malwarebytes, AdwCleaner, or HitmanPro to perform a more thorough scan and removal.
5. Delete Suspicious Files and Programs
Manually search for suspicious files or programs that FileRepMalware may have installed. This includes files that may have unusual names or have been placed in system directories without your knowledge. Deleting these files can prevent the malware from reinfecting the system. Carefully delete any suspicious files or programs that were identified during your scan.
6. Restore System Settings
If FileRepMalware has altered your system settings (e.g., changing your homepage, browser settings, or default search engine), restore them to their original configurations. You may also need to reset your passwords and logins if you suspect they have been compromised. Manually check and reset your browser and system settings to ensure no malicious changes remain.
7. Update Software and Apply Patches
After removing the malware, update all your software, including operating systems, browsers, and other programs. This ensures that any vulnerabilities that may have been exploited by the malware are patched, preventing reinfection. Enable automatic updates for all software and run a manual check for updates.
8. Monitor for Future Infections
After the removal process, monitor your system for any signs of reinfection. This includes monitoring system performance, checking for unusual network activity, and running regular antivirus scans. Continue scanning your system periodically and be vigilant for any signs of a new infection.
How to Prevent Future FileRepMalware Infections
Prevention is key to avoiding future FileRepMalware infections. By implementing the following strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of malware attacks:
1. Use a Reliable VPN
A VPN provides an added layer of security by encrypting your internet traffic and masking your IP address. This prevents cybercriminals from intercepting your communications and launching malware attacks through insecure networks. A VPN also ensures privacy while browsing the internet, especially on public Wi-Fi networks. Use AstrillVPN to secure your internet connection and protect against online threats.
2. Install and Update Antivirus Software
Ensure that you have reliable antivirus software installed and that it is updated. Modern antivirus programs can detect and block a wide range of malware, including FileRepMalware. Regularly updating your antivirus software ensures that it can identify the latest threats and effectively protect against them. Set up automatic updates and run regular full system scans.
3. Avoid Downloading Files from Untrusted Sources
Always download files from trusted sources, such as official websites, verified app stores, or known repositories. Avoid downloading files from suspicious or unfamiliar websites, as they may contain malware. Stick to reputable websites and avoid downloading pirated software or files shared through P2P networks.
4. Educate Users About Phishing and Social Engineering
Educating users about phishing and other social engineering tactics is one of the most effective ways to prevent FileRepMalware infections. Users should be cautious about opening email attachments or clicking on links in unsolicited emails, especially if the sender appears suspicious or unknown. Train employees and family members to recognize phishing attempts and avoid falling victim to malicious scams.
5. Enable Firewall Protection
A firewall can act as a barrier between your computer and the internet, preventing unauthorized access and blocking malware from spreading. Ensure that your system’s firewall is enabled and configured correctly. Enable the firewall on your computer and ensure it’s properly configured to block incoming threats.
6. Apply Security Patches and Updates Regularly
Software developers frequently release updates and patches to fix security vulnerabilities that malware could exploit. Make sure you apply these updates regularly to protect your system from known threats. Enable automatic software updates and manually check for updates if necessary.
7. Backup Important Files
Backing up your important files regularly ensures that you can restore your files without paying a ransom in case of a malware attack (like ransomware). Backup to an external hard drive or cloud storage, and keep your backups current. A reliable cloud backup service or external storage is used to back up essential files.
FAQs
Potentially Unwanted Programs (PUPs) are not always inherently dangerous, but they can pose risks. They may include bloatware, unwanted toolbars, or adware that can slow down your system, compromise privacy, or lead to unwanted pop-up ads. While not typically classified as malware, PUPs can degrade system performance and security.
Malicious software (malware) is a broad term for any software designed to harm or exploit a system. A virus is a specific type of malware that attaches itself to legitimate programs and spreads when the infected program is executed. While all viruses are malware, not all malware is a virus. Other types of malware include Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and worms.
No, a Trojan is not a file virus. A Trojan (or Trojan horse) is malicious software that disguises itself as a legitimate file or program but can perform harmful actions once executed. Unlike a virus, a Trojan does not replicate or spread by attaching to other files. Instead, it typically relies on social engineering to trick users into downloading and executing it.


No comments were posted yet