Wide area networks (WANs) connect geographically dispersed locations, enabling organizations to communicate and share data across different sites. As businesses expand and adopt cloud-based applications, the demand for efficient and reliable WAN technologies has increased significantly.
Two prominent WAN technologies exist Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) and Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS). SD-WAN and MPLS have emerged as leading solutions for organizations seeking to enhance network performance, optimize costs, and improve overall connectivity.
Follow this guide thoroughly to learn more about SD-WAN and MPLS and see which one is best for you.
Table of Contents
What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN, or Software-Defined Wide Area Networking, is a modern networking approach that enhances wide-area networks’ performance, agility, and cost-effectiveness. Unlike traditional WAN architectures that rely on dedicated hardware, SD-WAN leverages software-defined networking principles to abstract the control plane from the underlying network infrastructure.
SD-WAN Characteristics
- SD-WAN enables businesses to dynamically manage and control their network infrastructure through a centralized management platform. This flexibility allows for the efficient allocation of network resources, rapid deployment of new sites, and the ability to adapt to changing business needs.
- By leveraging multiple network links, such as broadband internet, MPLS, or 4G/5G connections, SD-WAN optimizes costs by intelligently routing traffic based on performance requirements and cost considerations. This approach reduces reliance on expensive dedicated circuits and saves costs without compromising performance.
- SD-WAN employs advanced traffic management techniques, including real-time path selection, prioritization, and quality of service (QoS) mechanisms. This optimization ensures critical applications receive the necessary bandwidth and low latency, enhancing performance and user experience.
- SD-WAN integrates robust security features like encryption, firewall capabilities, and threat intelligence. Centralized security policies and advanced threat detection help protect the network against cyber threats, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity across the WAN.
How SD-WAN Works?
SD-WAN creates an overlay network that abstracts the underlying physical network infrastructure. It typically consists of two key components: edge devices or appliances deployed at each site and a centralized controller that manages the network.
The edge devices establish secure tunnels over various transport options, such as MPLS, broadband, or cellular networks. These tunnels encapsulate and encrypt data traffic, ensuring secure communication between sites. The centralized controller provides a unified view of the network and applies policies to optimize traffic routing, prioritization, and security measures.
What is MPLS?
Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a widely used technique in telecommunications and networking for efficient data packet forwarding. It operates at the network layer of the OSI model and allows routers to make forwarding decisions based on labels attached to packets rather than examining the entire packet header.
MPLS Characteristics
- MPLS offers robust QoS capabilities, enabling network administrators to prioritize traffic and allocate resources based on application requirements. This ensures critical applications, such as voice and video, receive the necessary bandwidth and low latency for optimal performance.
- MPLS allows for traffic engineering, which involves optimizing network traffic routing to utilize network resources efficiently. This capability enables network administrators to control and manage traffic flows, balance network loads, and improve overall performance.
- MPLS networks are highly scalable, making them suitable for organizations with numerous branch offices or complex network topologies. MPLS provides a reliable and predictable forwarding mechanism, ensuring consistent performance and minimizing packet loss.
- MPLS inherently offers security by isolating customer traffic within the service provider’s network. As packets are encapsulated and labeled, they remain separated from other customer traffic, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or interception.
How MPLS Works?

MPLS operates by adding a label to each packet’s header as it enters the service provider’s network. This label contains information that directs the packet’s path through the network. Instead of performing a traditional routing lookup based on the packet’s destination IP address at each router, MPLS routers only need to examine the label.
Upon entering the MPLS network, the first router assigns a label to the packet and forwards it based on that label. Each subsequent router along the path makes forwarding decisions based on the label without the need for deep packet inspection. This label-switching mechanism ensures efficient and fast packet forwarding.
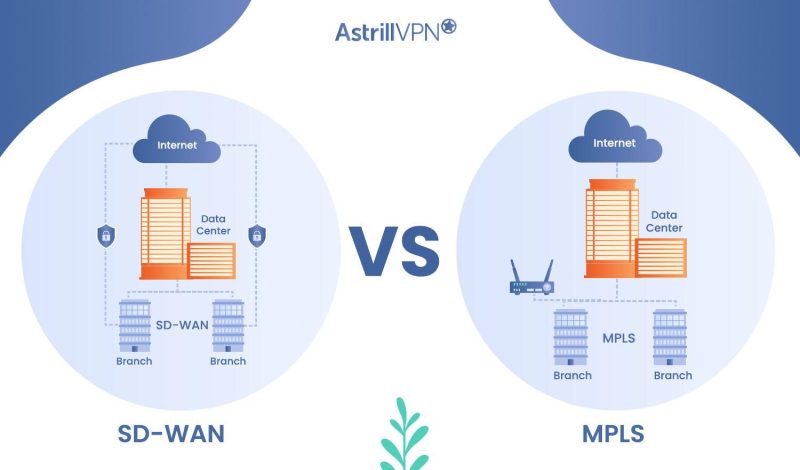
SD-WAN vs MPLS: Head-to-Head Differences
If you’re still wondering “is SD WAN better than MPLS,” then this head-to-head comparison will clear all your doubts:
| SD-WAN | MPLS | |
| Network performance (Bandwidth and latency) | Utilizes multiple transport options, including broadband internet, for increased bandwidth and potential for higher latency. | Offers predictable and consistent performance, ensuring low latency and high bandwidth. |
| Quality of Service (quality of service) and traffic prioritization | Provides advanced QoS capabilities to prioritize critical applications, guaranteeing optimal performance and minimal packet loss. | Offers robust quality of service mechanisms to prioritize traffic based on labels, guaranteeing quality for critical applications. |
| Redundancy and failover capabilities | Enables automatic failover and redundancy across multiple links, ensuring seamless network connectivity in case of link failures. | Supports redundancy through backup circuits or diverse paths to maintain high availability in the event of link failures. |
| Ability to adapt to changing business requirements | Offers agility to adapt to evolving business needs, allowing for seamless integration of new technologies and services. | Requires coordination with service providers for changes, potentially leading to slower adaptation to changing requirements. |
| Ease of adding or removing network locations | Simplifies the addition and removal of network locations through centralized management, reducing deployment complexities. | Involves coordination with service providers for adding or removing network locations, potentially requiring longer lead times. |
| Centralized control and visibility | Offers centralized management and visibility of the entire network, allowing for easier control and monitoring of network traffic. | Provides centralized control and visibility, simplifying network management and facilitating policy enforcement. |
| Ease of network management and configuration | Streamlines network management through intuitive interfaces and automation tools, reducing manual configuration efforts. | Requires manual configurations and coordination with service providers for changes and adjustments in the network. |
| Encryption and data protection | Incorporates robust encryption mechanisms to ensure data privacy and protection during transmission across the network. | Provides inherent security through isolated networks, but additional encryption mechanisms may be required for data protection. |
| Threat detection and mitigation | Offers advanced threat detection and mitigation features to identify and mitigate potential security risks and attacks. | Requires additional security measures and devices to detect and mitigate threats effectively. |
SD-WAN vs MPLS Cost Comparison
Here’s a difference between SD-WAN and MPLS costs, which will help you understand which one is costlier and a viable option for you.
| SD-WAN | MPLS |
| SD-WAN typically requires an initial investment in hardware or virtual appliances to deploy at each branch location. | MPLS generally requires expensive networking hardware, such as routers and switches to establish the MPLS network. |
| SD-WAN can potentially offer cost savings in terms of ongoing operational expenses. | MPLS typically incurs ongoing costs, including service charges for maintaining the dedicated MPLS circuits and network equipment. |
| SD-WAN offers better cost scalability as organizations expand their network. | Adding new branch locations or increasing bandwidth capacity often requires additional MPLS circuits, resulting in higher expenses. |
SD-WAN Pros and Cons
Following are some pros and cons of SD-WAN:
Pros
- SD-WAN offers enhanced agility, allowing organizations to quickly adapt and respond to changing business needs.
- It can significantly reduce costs compared to traditional MPLS networks.
- It utilizes advanced traffic management techniques to optimize performance.
- SD-WAN offers flexibility in network design and scalability.
- It provides centralized control and visibility over the entire network.
Cons
- SD-WAN relies on various Internet connections, including broadband, which may be less reliable than dedicated circuits.
- While SD-WAN incorporates security features like encryption and firewall capabilities, relying on public internet connections introduces additional security risks.
MPLS Pros and Cons
Following are some pros and cons of SD-WAN:
Pros
- Networks based on MPLS provide predictable and reliable performance, making them suitable for applications that require consistent bandwidth, low latency, and minimal packet loss.
- MPLS inherently provides a secure communication infrastructure by isolating customer traffic within the service provider’s network.
- It has a proven track record of reliability and performance, and many businesses already have MPLS networks in place, making it a familiar and trusted choice.
- MPLS service providers often offer SLAs that guarantee specific performance levels, uptime, and support.
Cons
- Dedicated circuits and service provider charges can be expensive, making MPLS less cost-effective for small to medium-sized businesses or organizations with budget constraints.
- Adding new network locations or increasing bandwidth in MPLS networks may require coordination with service providers and longer lead times.
- MPLS networks are traditionally more static and require manual configurations for network changes.
- Integrating cloud services and fully leveraging the benefits of cloud computing can be more challenging than SD-WAN.
SD-WAN vs. VPN: Which one’s better?
SD-WAN and VPN are two different technologies that serve different purposes. It’s not a matter of one being better than the other, but rather understanding their specific use cases and choosing the appropriate technology based on your organization’s requirements. Here’s a comparison between SD-WAN and VPN to help you understand their differences:
| SD-WAN | VPN | |
| Purpose | Optimizing network connectivity and performance | Providing secure and encrypted communication |
| Functionality | Dynamically routes traffic, selects best path | Establishes encrypted tunnel for secure communication |
| Benefits | Enhanced agility, cost savings, centralized management | Secure remote access, data encryption, privacy protection |
| Primary Use Cases | Branch connectivity, application performance optimization | Remote work, secure network access |
| Network Focus | Wide Area Network (WAN) | Network Security |
| Performance | Optimizes traffic routing for better performance | No direct impact on network performance |
| Security | Provides basic security features | Focuses on data encryption and privacy |
| Flexibility | Adapts to changing business requirements | Limited flexibility beyond secure access |
| Cost | Cost savings through intelligent traffic routing | Cost-effective remote access solution |
In simpler terms, if you’re looking for a solution for personal network and remote accessibility, then opt for AstrillVPN. However, if you want a security solution that can secure your WAN, then opt for SD-WAN.
MPLS vs. VPN: Which one’s better?
| MPLS | VPN | |
| Purpose | Provides reliable and predictable WAN connectivity | Enables secure and encrypted communication |
| Functionality | Utilizes dedicated circuits and packet labeling | Establishes encrypted tunnels for data transmission |
| Benefits | Reliable performance, low latency, strong security | Secure remote access, data encryption, privacy |
| Primary Use Cases | Interconnecting geographically dispersed locations | Remote work, branch office connectivity, secure access |
| Network Focus | Wide Area Network (WAN) | Network Security |
| Performance | Predictable performance with low latency | Performance varies based on internet connection quality |
| Security | Limited security features | Strong encryption and secure communication |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, longer lead times for network changes | Provides flexibility in establishing secure connections |
| Cost | Higher upfront costs, ongoing service charges | Generally more cost-effective option |
Conclusion
Both SD-WAN and MPLS are popular wide area network (WAN) technologies that offer unique advantages for organizations. SD-WAN provides agility, cost savings, scalability, and enhanced application performance optimization, making it well-suited for organizations with multiple branch locations and evolving network requirements.
On the other hand, MPLS offers reliable and predictable performance, low latency, and strong security, making it a preferred choice for organizations that prioritize consistent network performance and have latency-sensitive applications.
It is recommended to conduct a thorough analysis of your organization’s needs, consult with networking experts, and evaluating various vendors and service providers to make an informed decision. The decision should be based on the unique requirements, goals, and constraints of the organization.
FAQs
SD-WAN can be used as an alternative to MPLS, but it does not necessarily replace it entirely. Organizations have the option to deploy SD-WAN as a standalone solution or in combination with existing MPLS networks, creating a hybrid approach that optimizes performance, cost, and flexibility.
SD-WAN can provide a high level of security when properly implemented. While MPLS has inherent security benefits due to its private network infrastructure, SD-WAN can achieve comparable security levels through strong encryption and secure communication protocols.
No, SD-WAN is not just VPN. While both technologies can provide secure connectivity, they have distinct functionalities.
The three types of MPLS are:
LDP (Label Distribution Protocol)
RSVP-TE (Resource Reservation Prot is recommended, consultingfic Engineering)
MP-BGP (Multiprotocol Border Gateway Protocol)


No comments were posted yet