Proxy vs. VPN: What Should I Use? [Updated]

Arsalan Rathore
![Proxy vs. VPN: What Should I Use? [Updated]](https://www.astrill.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/proxy-vs-vpn-1-731x470.jpg)
Since VPNs and proxy servers both redirect user data to a server and conceal their real IP address, it’s easy to put them against one another to deem which could be a better fit. However, one is superior to the other for reasons which we will elaborate on in this post.
Table of Contents
What is a Proxy?
Proxy servers operate as intermediaries between your device and the website you’re accessing. Since your connection with the host server is diverted through a middle-man, which is a remote device, your actual IP address remains hidden from websites. They simply redirect traffic that originates from an app since they function at the level of one application.
A proxy fulfills the bare-minimum requirements of security and secrecy by hiding the user’s actual IP address. It does not encrypt traffic or ensure a secure connection, especially outside of the application it has been connected to.
What is a VPN?
A VPN connects the user to a VPN server of their choosing. This means that any incoming or outgoing traffic is rerouted in a channel that is created between the user’s device and their online activities. As such, their data is encrypted, and their IP address reflects that of their VPN server.
Most VPN service providers offer numerous server locations, which allow for a more sophisticated and secure experience. VPNs also mostly work on a system level, which means that all sorts of traffic will be protected and encrypted.
This means that even network administrators such as your Internet Service Provider will not be able to monitor your browsing activity. This can help alleviate the effects of network regulations such as geo-restrictions and ISP speed throttling.
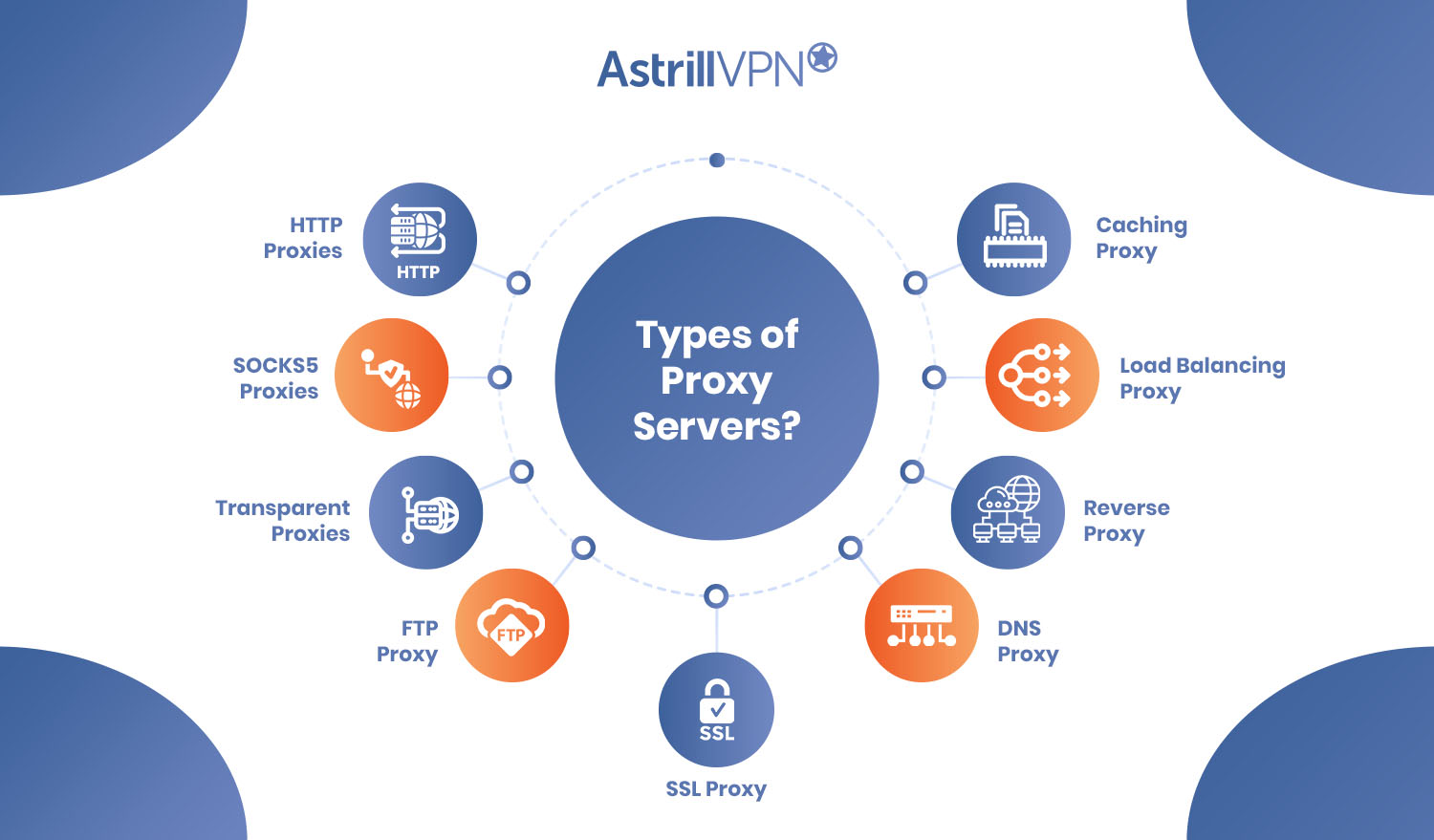
Types of Proxy Servers?
Proxies only work on one website or application at a time. Users can take advantage of the multiple types of proxy servers available for them to utilize.
HTTP proxies
These proxies are only functional with websites and web pages. Users can configure their browser to an HTTP proxy server, which can allow them to bypass any censorship they may face, such as geo-restrictions.
SOCKS5 proxies
These proxies are functional with websites and applications. Since they are more popular in use, they are a bit slower than HTTP proxies. But since they are so commonly used, they can handle a variety of data traffic, ranging from file sharing to online gaming.
SOCKS proxies are considered to be the best type of proxy because of their ability to bypass geo-restrictions easily and the fact that they are more secure than the other proxies.
Transparent proxies
What makes transparent proxies special is that users are rarely made aware of the fact that they are being used. These proxies are most popular with organizations, such as companies and colleges, who need to monitor and regulate the online activity of their employees or students. They are also put in place to save bandwidth and ensure appropriate usage of the connection.
FTP Proxy
An FTP (File Transfer Protocol) proxy is a proxy server that acts as an intermediary between a user and an FTP server. The FTP proxy can control and monitor FTP traffic and can help prevent unauthorized access and data theft. FTP proxies are often used in enterprise environments to enforce security policies and ensure compliance with regulations.
SSL Proxy
An SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) proxy is a proxy server designed to intercept and encrypt traffic between a client and a server. SSL proxies are often used to secure web traffic and protect sensitive data such as passwords and credit card information. SSL proxies are commonly used in corporate environments to protect against network eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
DNS Proxy
A DNS (Domain Name System) proxy is a proxy server that intercepts DNS queries and redirects them to a different DNS server. DNS proxies are often used to bypass censorship or to improve network performance by caching DNS responses. DNS proxies can also be used to implement security controls such as filtering or blocking access to malicious websites.
Reverse Proxy
A reverse proxy is a type of proxy server that sits between a client and a web server. Unlike a forward proxy, which is used to access resources on the internet on behalf of a client, a reverse proxy is used to provide a layer of protection and optimization for a web server.
When a client sends a request to a web server protected by a reverse proxy, the request first goes to the reverse proxy server, which then forwards the request to the web server.
This helps to protect the web server from direct exposure to the internet, as the reverse proxy can be configured to filter and block malicious traffic before it reaches the web server. Additionally, a reverse proxy can be used to improve the performance of a web server by caching content and serving it directly to clients without requiring the web server to generate the content on each request.
Load Balancing Proxy
A load-balancing proxy is a type of proxy server that is specifically designed to distribute incoming traffic across multiple servers on the back end. Like a reverse proxy, a load-balancing proxy sits between a client and a server, but instead of simply forwarding requests and responses, it actively manages the distribution of traffic to ensure that no one server is overloaded.
Caching Proxy
A caching proxy serves as an intermediary between a client computer and a remote server. The primary function is improving performance by caching frequently requested content. Whenever a client requests a web page or other content from a remote server, the caching proxy intercepts the request and checks to see if a cached copy of the requested content is available.
If a cached copy is found, the caching proxy serves the cached content to the client without fetching it from the remote server. This process reduces the time it takes to load content, reduces network bandwidth usage, and minimizes the load on the remote server.
The main differences between VPN and Proxy Services
Proxy servers function on the basis of an application or software. VPNs run on the device level. They can change the user’s IP address without encrypting their traffic, as their data is routed through proxy servers. For VPNs, the user connects to a VPN server, allowing for data encryption and IP masking.
Proxies aren’t well regarded as privacy tools. They exist mostly for security purposes or for anonymity. Some of their most common uses are bypassing or imposing restrictions. If you have ever been unsuccessful at accessing your favorite websites when using a library computer, know that that is the work of a proxy server!
Since VPNs primarily encrypt user data and traffic, they are considered privacy tools before anything else. That’s why AstrillVPN offers a variety of features to enhance user experience and protect their connection.
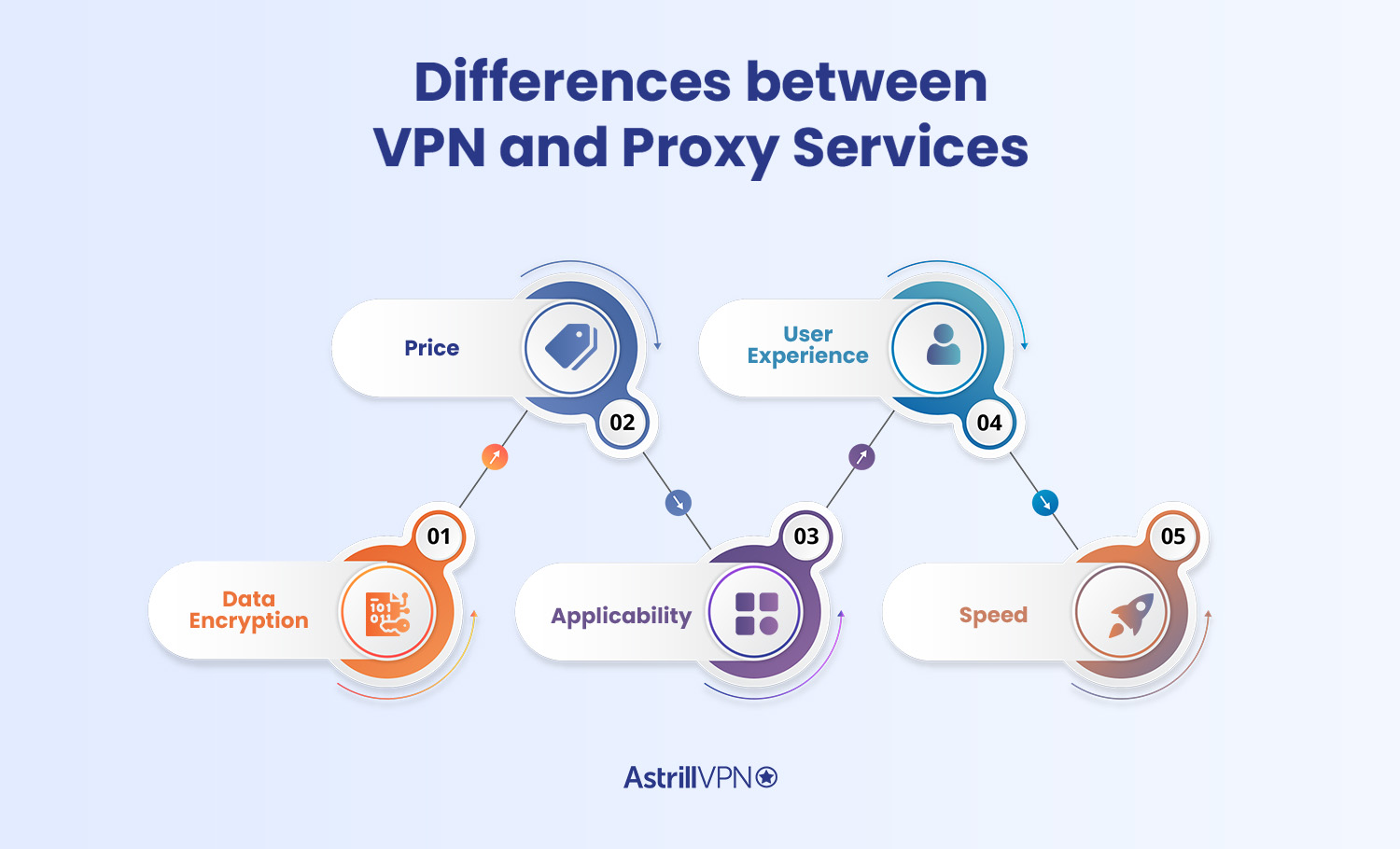
Despite their commonality of protecting user identities and bypassing restrictions, one stark difference is that VPNs protect user privacy in a way that proxy services can not. Here are some other differences that they have:
1. Data Encryption
VPNs encrypt user data and traffic to shield them from ISP throttling, website trackers, government censorship, network surveillance, and more. Proxies can not and do not encrypt user traffic.
2. Price
Anything that is given for free usually has costly consequences. It is expensive to maintain VPN servers, but web proxies are almost always free. Free VPNs exist as well, but there’s a difference in the way user privacy is guaranteed.
3. Applicability
VPNs work on all applications installed on a particular device, giving the user system-wide security and protection. Proxies, on the other hand, only reroute traffic of a single, specified application or webpage.
4. User Experience
As opposed to VPNs, proxies are much smaller operations that don’t have a real support network. Companies run VPNs, and due to their payment packages, they have the opportunity to offer customer support to their users. This makes VPNs much more reliable than proxies.
5. Speed
VPNs take a while to connect to a VPN server and ensure all protocols are in order to guarantee user security. Proxies, on the other hand, span over a much smaller area of functioning and, thus, typically work faster. That being said, a good quality VPN application can bypass ISP throttling and allow for a safer and speedier experience in contrast to a proxy server.
Read Also: Are VPNs Legal or Illegal in 2022?
Pros and Cons of a VPN
We mentioned all the important pros and cons of VPN below:
Pros:
- Data and Connection Encryption
- System-wide functioning
- Reliable customer support and connection
- Bypass restrictions
- Hides IP address
- Additional features for enhanced security
- User-friendly and supportive
- Unbeatable security protocols
- No-log policy
Cons:
- Speeds may sometimes be slower than a proxy
Pros and Cons of a Proxy Server
Pros:
- Almost always free
- Speedier than a VPN
- Hides IP address
- Can bypass and enforce restrictions
Cons:
- Data is not secure
- Can’t unblock streaming services
- Only works on one application at a time
- No customer support
- Hard to configure and maintain
Proxy vs. VPN: Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | Proxy | VPN |
| Encryption | None or basic | Strong encryption |
| IP Address | Uses the IP address of the proxy server | Hides user’s IP address |
| Security | Less secure as traffic is not encrypted | More secure as traffic is encrypted |
| Speed | Faster as it doesn’t encrypt traffic | Slower due to encryption |
| Privacy | Provides some level of privacy by hiding IP address | Provides a high level of privacy by encrypting traffic and hiding IP address |
| Geo-restrictions | Can bypass some geo-restrictions | Can bypass more geo-restrictions |
| Compatibility | Compatible with most applications and devices | Compatible with most applications and devices |
| Cost | Free or low-cost | May require a subscription fee |
| Logging | Some proxies log user activity | Some VPNs log user activity |
| Ease of use | Easy to use with no installation required | It may require installation and configuration |
Why Do You Need a Proxy or a VPN
The main concern of some VPN and proxy users is security and privacy. Other reasons can include needing to bypass geographic restrictions or hiding one’s own IP address. For these two reasons, a proxy is sufficient. However, when user security and privacy is the concern, VPNs out perform proxy servers.
When connecting to an unsecured network, all data transmitted will still be vulnerable to theft or losses if a proxy server is used. The website you’re accessing through the server may not be able to see your IP address, but your data will still be accessible to third parties.
VPNs work best as a safe, easy-to-use, and truly secure solution to users’ concerns about privacy. It is also a better investment in the long run, as you will rarely need to configure things by yourself. VPNs are superior in customer support, user accessibility, and interface, and they also protect the whole device as they are not confined to one program or webpage.
Do you need a proxy if you have a VPN?
You do not need a proxy if you already use a VPN. That is because your VPN re-routes your traffic through a VPN server, which masks your IP address and bypasses restrictions and censorship in one go. Adding a proxy server on top of a VPN would render the proxy futile and may result in even slower speeds.
Which One Should You Use?
A high-quality VPN, like AstrillVPN, offers unbeatable benefits over any type of proxy server. Astrill provides better encryption and user security, even when torrenting, and greater stability in all types of connections. Your online activities will be protected from hackers and third parties due to high levels of encryption and a no-log policy.
AstrillVPN is unquestionably the best security solution available on the market. A VPN is the way to go if your primary concern lies in online security and privacy.
FAQs
You can use a proxy and VPN together, but it’s generally not recommended. While a VPN provides encryption and hides your IP address, using a proxy may complicate the connection and slow your internet speed. Additionally, combining both might cause issues with stability and security, as proxies do not offer the same level of encryption as VPNs.
When using a VPN, your IP address is masked, and your internet traffic is encrypted, making it very difficult to track. However, while the VPN hides your activity from most external observers, your VPN provider can still see your online behavior. Choosing a VPN provider with a strict no-logs policy is important to ensure that your browsing activities are not being tracked or stored.
Yes, a proxy can track your internet history, depending on the proxy type and policies. Unlike a VPN, most proxies don’t encrypt your data, meaning the proxy server can log your browsing activities. If privacy is your main concern, a VPN is a better option as it encrypts your connection and keeps your activity private.
Yes, a VPN can replace a proxy and is generally considered the superior option. A VPN offers all the benefits of a proxy masking your IP address but also provides encryption for your data, ensuring your online activity remains private and secure. While proxies are useful for basic IP masking, they provide a different level of security than a VPN.
Yes, proxies are generally cheaper than VPNs, and some are even free. However, the cost savings come at the expense of security and privacy. VPNs offer much more robust encryption, privacy features, and reliability, making them a better investment for most users who prioritize security.

No comments were posted yet