Understanding Network Security Threats: Types, Risks and Detection

Bisma Farrukh

As you navigate the complex landscape of modern cybersecurity, understanding and combating network security threats is paramount. Your organization’s digital infrastructure faces an ever-evolving array of risks in today’s interconnected world. From sophisticated malware to social engineering tactics, the threats to your network’s integrity are diverse and relentless. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to effectively identify, prevent, and mitigate these dangers. By exploring the latest trends in cybercrime and implementing robust security measures, you’ll be better prepared to safeguard your valuable data and maintain the trust of your stakeholders in an increasingly perilous digital environment.
Table of Contents
What is a Network Security Threat?
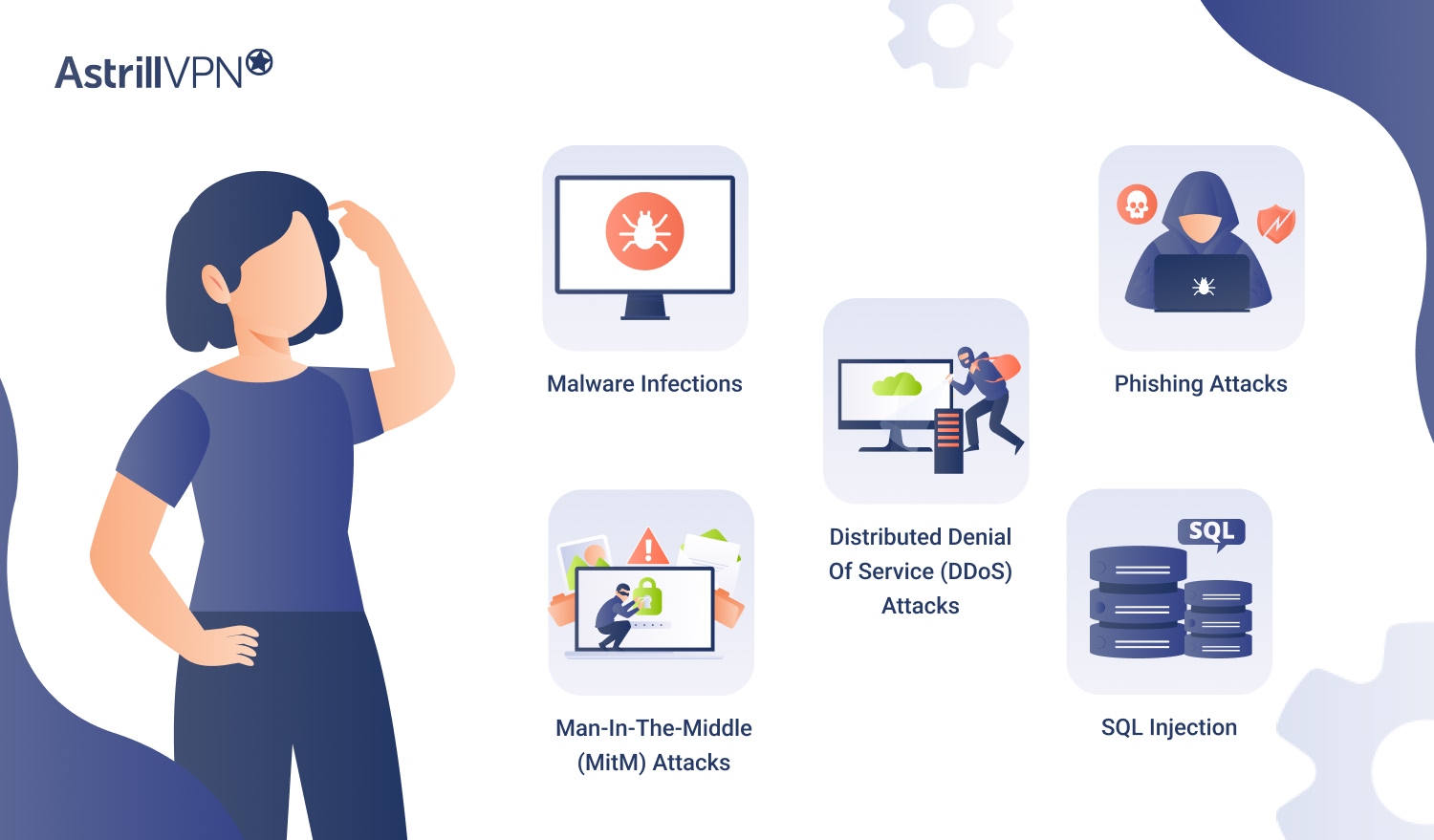
A network security threat is any potential danger to your organization’s network infrastructure, data, or users. These threats can come from various sources, both internal and external, and aim to exploit vulnerabilities in your system. Network security threats encompass a wide range of malicious activities, including:
- Malware infections (viruses, worms, trojans)
- Phishing attacks
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks
- SQL injection
Understanding these threats is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. By identifying potential risks, you can implement appropriate safeguards to protect your network’s integrity, confidentiality, and availability. Network security threats are constantly evolving, so staying informed about the latest attack vectors and vulnerabilities is essential for maintaining a robust defense posture.
Understanding the Most Common Network Security Threats
In today’s digital landscape, network security threats are constantly evolving. Malware, including viruses, worms, and trojans, remains a persistent danger, infecting systems and stealing sensitive data. Phishing attacks continue to trick users into divulging confidential information through deceptive emails and websites.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs are sophisticated, long-term attacks that often target high-value organizations. These threats can remain undetected for extended periods, siphoning off valuable data.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
DDoS attacks overwhelm networks with traffic, rendering services inaccessible. These attacks can cripple businesses, causing significant financial losses and reputational damage.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks
MitM attacks intercept communications between two parties, potentially exposing sensitive information. These threats are particularly dangerous on unsecured public Wi-Fi networks.
Understanding these common threats is crucial for developing robust network security strategies and safeguarding your digital assets.
Major Types of network security threats
Network security threats come in various forms, each targeting different vulnerabilities in your system. Understanding these threats is crucial for effective protection.
Botnets & Worms
Botnets are networks of compromised computers controlled by malicious actors, while worms are self-replicating malware that spread across networks.
Viruses
Viruses attach themselves to legitimate files and programs, causing damage when executed.
Pharming
Pharming attacks redirect users to fraudulent websites, compromising sensitive information.
Logic Bombs
Logic bombs are malicious code segments triggered by specific conditions, potentially causing severe system damage.
Ransomware
Ransomware encrypts data and demands payment for its release, often targeting critical infrastructure and businesses.
Malware
Malware encompasses a wide range of harmful programs, including viruses, worms, trojans, and ransomware. These threats can infiltrate your network, steal data, or disrupt operations.
Phishing attacks
Phishing remains a prevalent threat, using deceptive emails or websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information. These attacks often mimic legitimate sources, making them particularly dangerous.
Denial of Service (DoS)
DoS attacks aim to overwhelm your network resources, rendering services unavailable. Distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks use multiple sources, making them harder to mitigate.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM)
MitM attacks intercept communications between two parties, potentially allowing attackers to eavesdrop or alter data in transit. These threats can compromise sensitive information and transactions.
Network security threats and vulnerabilities
Network security vulnerabilities pose significant risks to organizations of all sizes. Malicious actors can exploit potential weaknesses in your digital infrastructure, leading to data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Common threats
Some prevalent network security threats include:
- Malware: Viruses, worms, and trojans that can infect systems
- Phishing: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information
- DDoS attacks: Overwhelming networks with traffic to disrupt services
- Man-in-the-middle attacks: Intercepting and altering communications
Vulnerabilities to address
Key vulnerabilities often stem from:
- Outdated software and unpatched systems
- Weak passwords and poor access controls
- Misconfigured network devices and firewalls
- Lack of encryption for sensitive data
Understanding these threats and vulnerabilities is crucial for developing a robust network security strategy.
Proactive Threat Detection and Incident Response Strategies
In today’s ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape, organizations must adopt proactive measures to safeguard their networks. Implementing robust threat detection systems and incident response protocols is crucial for maintaining a strong security posture.
Advanced Threat Detection Techniques
Utilize machine learning algorithms and behavioral analytics to identify anomalous network activity. Deploy next-generation firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS) to monitor traffic patterns and flag potential threats in real time.
Incident Response Planning
Develop a comprehensive incident response plan that outlines clear procedures for:
- Identifying and containing security breaches
- Mitigating damage and preserving evidence
- Notifying stakeholders and regulatory bodies
- Conducting post-incident analysis and improving defenses
Regular tabletop exercises and simulations help ensure your team is prepared to respond swiftly and effectively to a security incident.
Network security infrastructure
Your network security infrastructure forms the foundation of your defense against cyber threats. This multi-layered approach combines hardware, software, and policies to protect your digital assets.
Key components
The firewall is at the core of your infrastructure, acting as a gatekeeper between your internal network and the outside world. Intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) monitor network traffic for suspicious activity, while virtual private networks (VPNs) encrypt data in transit.
Layered defense strategy
Implement a defense-in-depth strategy by deploying multiple security measures. This includes network segmentation to isolate sensitive data, regular software patching, and robust access controls. Utilize encryption for data at rest and in motion to safeguard against unauthorized access.
By carefully designing and maintaining your network security infrastructure, you create a resilient barrier against evolving cyber threats.
How AstrillVPN can help prevent network security threats?
AstrillVPN offers robust protection against various network security threats, safeguarding your online activities and sensitive data. Encrypting your internet traffic creates a secure tunnel that shields your information from prying eyes and potential cyber attacks. This powerful tool masks your IP address, making it significantly harder for hackers to target your devices or track your online movements.
Enhanced protection features
AstrillVPN employs advanced security protocols and military-grade encryption to fortify your digital defenses. Its kill switch feature ensures that your data remains protected even if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly. Additionally, the service’s no-logs policy adds an extra layer of privacy, preventing your online activities from being recorded or potentially compromised.
Implementing Robust Network Security Measures
Layered Defense Strategy
- Adopt a multi-layered approach to network security.
- Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and virtual private networks (VPNs) to create multiple barriers against threats.
- Update and patch all systems regularly to address vulnerabilities promptly.
Access Control and Authentication
- Enforce strong password policies and implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) across your network.
- Utilize role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure users only have access to resources necessary for their job functions.
- Regularly audit user accounts and permissions to maintain tight control over network access.
Continuous Monitoring and Incident Response
- Deploy network monitoring tools to detect anomalies and potential security breaches in real-time.
- Establish a comprehensive incident response plan to quickly address and mitigate threats when they occur.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address weaknesses in your network infrastructure.
Conclusion
Network security threats are constantly evolving, requiring vigilance and proactive measures to protect your organization’s digital assets. By understanding the various types of threats and implementing a multi-layered security approach, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to attacks. While no system is completely impenetrable, your diligence in following the strategies outlined in this guide will go a long way in safeguarding your network. With the right tools, knowledge, and mindset, you can create a robust defense against even the most sophisticated cyber threats.
FAQs
The most prevalent network security threats include malware infections, phishing attacks, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. Malware encompasses viruses, trojans, and ransomware that can compromise system integrity. Phishing schemes trick users into divulging sensitive information, while DDoS attacks overwhelm networks with traffic to disrupt services.
Implement a multi-layered security approach including:
Regular software updates and patch management
Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication
Comprehensive firewall and antivirus protection
Employee cybersecurity training and awareness programs
Network segmentation and access controls
Additionally, consider investing in advanced threat detection systems and engaging in regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities.
Immediately isolate affected systems to prevent further spread. Engage your incident response team or cybersecurity professionals to assess the breach’s extent. Preserve evidence for forensic analysis and potential legal action. Once the threat is contained, conduct a thorough security audit, update your defenses, and strengthen your incident response plan for future preparedness.

No comments were posted yet