When troubleshooting network issues or configuring your home router, one crucial piece of information you’ll need is the router’s IP address. A router’s IP address is the gateway between your home network and the internet, allowing devices to communicate with external networks.
Knowing how to locate this IP address empowers you to access your router’s settings, manage security features, and optimize network performance. In this guide, we’ll cover step-by-step instructions for finding your router’s IP address across different devices, ensuring smooth network management.
Table of Contents
What Is My Router IP Address?
A router’s IP address, commonly called the “default gateway,” is a unique numerical label assigned to the router that acts as the central hub for communication within your local network. The router’s IP is part of a private IP range (192.168.x.x), used solely for local networks, as defined by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
This IP address is vital for routing traffic between devices in your network and the Internet. It enables you to configure settings such as firewall rules, parental controls, and even the integration of VPN services.
Why Should I Know My Router’s IP Address?
Knowing your router’s IP address is important for several reasons, especially when it comes to managing your home or office network. Here are key reasons why you should be familiar with it:
1. Access Router Settings
The router’s IP address is the gateway to its control panel. You need it to access the router’s administrative interface, where you can:
- Change the Wi-Fi name (SSID) and password.
- Update security settings like enabling WPA3 or configuring a firewall.
- Manage parental controls and block certain websites or devices.
- Set up a guest network for visitors without giving them access to your main network.
2. Configure Advanced Settings
Many advanced router configurations, such as port forwarding, static IP settings, and Dynamic DNS (DDNS), require you to log into the router using its IP address. These settings are useful for:
- Hosting a website or game server.
- Ensuring certain devices always get the same IP on your local network.
- Allowing access to your home network from remote locations.
3. Troubleshooting Connectivity Issues
Knowing your router’s IP address helps when diagnosing connectivity problems. For example, if your internet isn’t working, you can log into your router and check its status to determine if the problem is with the router or your ISP. Additionally, you can reboot the router, check connected devices, or view logs for errors that can provide insight into network issues.
4. Setting Up a VPN
If you want to set up a VPN on your router for network-wide privacy, you’ll need the router’s IP address to configure it. This setup ensures that all devices on your network are protected by the VPN, even those that don’t support VPN apps (like smart TVs or game consoles).
5. Improve Security
Logging into your router using its IP address enhances your network’s security. You can:
- Change default credentials to prevent unauthorized access.
- Update firmware to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Monitor connected devices to identify any unknown connections.
6. Managing Bandwidth
Some routers allow you to monitor or manage bandwidth usage through their interface. This is useful if you want to limit the internet speed for certain devices or prioritize traffic for specific applications (like streaming or gaming).
Where to Find IP Address on Router on Different Devices
Windows
To find your IP address on router on Windows, there are two straightforward methods:
Using Command Prompt:
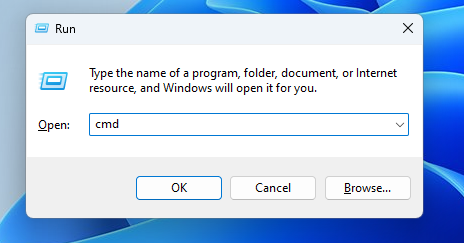
- Press Windows + R, type “cmd” and press Enter.
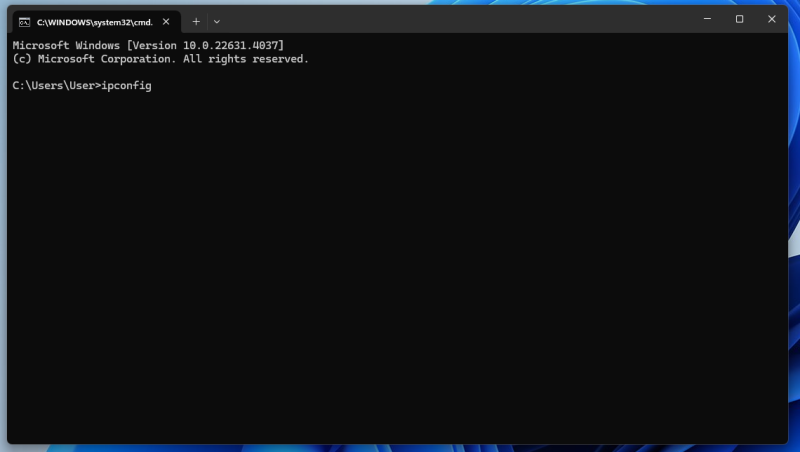
- In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig and press Enter.
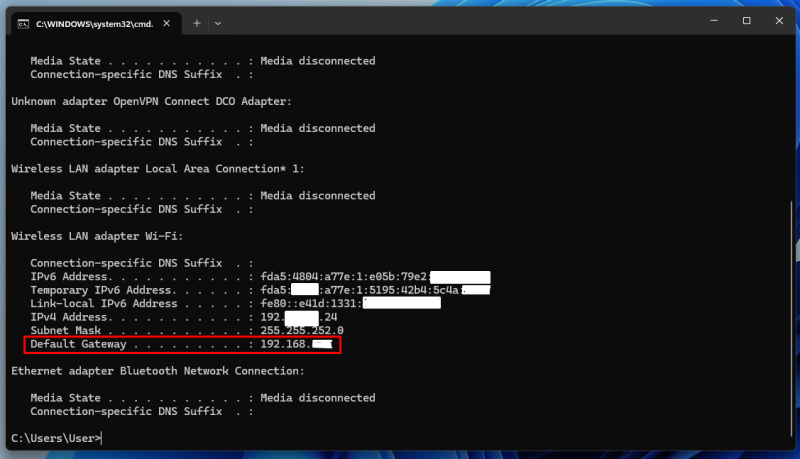
- Scroll through the results and locate “Default Gateway,” which displays your router’s IP address.
Through the Control Panel:
- Go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center.
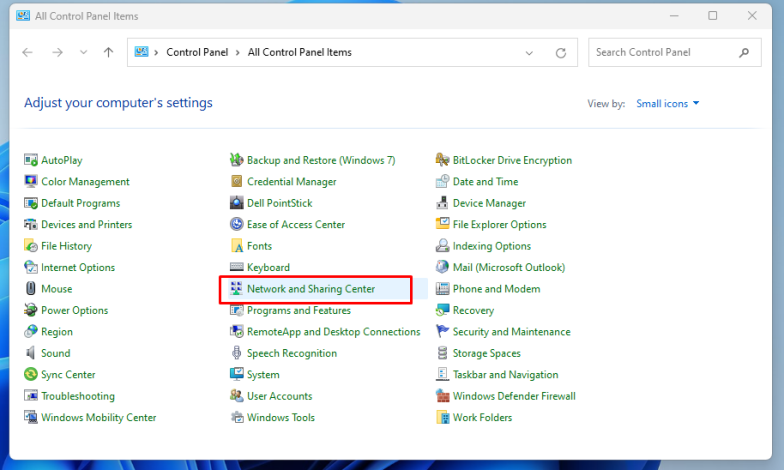
- Click on the name of your network next to “Connections.”
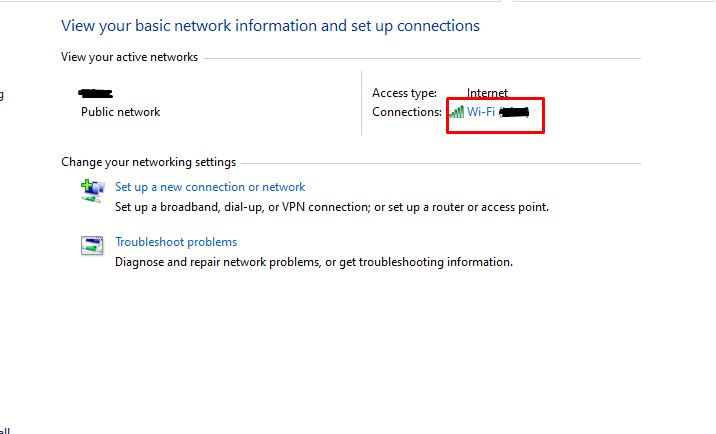
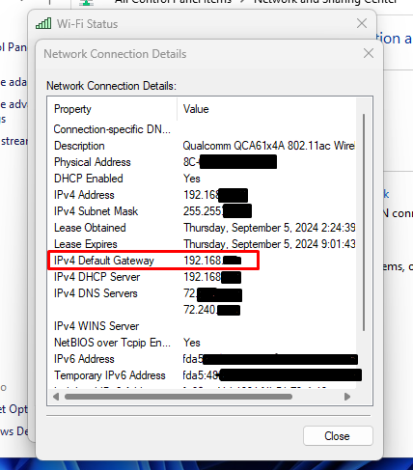
- In the new window, click “Details” to find the router’s IP next to “IPv4 Default Gateway.”
Mac OS
On a Mac, you can find your router’s IP address by following these steps:
- Click the Apple logo in the top-left corner of your screen and go to System Preferences.
- Select Network, then click Wi-Fi in the left panel.
- Click “Advanced” and navigate to the TCP/IP tab, where your router’s IP is listed next to “Router.”
Linux
- Click on the network icon in your taskbar and select “Network Settings.”
- Choose your connected network, click “Details,” and find the router’s IP under the “Gateway” or “IPv4” section.
How to find my Router IP Address from Mobile?
iPhone/iPad (iOS)
- Open the Settings app and tap Wi-Fi.
- Tap the information icon (i) next to your network.
- Scroll down, and your router’s IP address is listed under “Router.”
Android
- Go to Settings > Network & Internet > Wi-Fi.
- Tap the gear icon next to your connected Wi-Fi network.
- Scroll down to “Advanced,” and under “Gateway,” your router’s IP address will be displayed.
How to Find Your Router’s Public IP Address?
There are several easy methods to find your router’s public IP address (the IP address that is visible to external networks or websites). Here’s a detailed, professional guide:
Method 1: Using Astrill’s “What is my IP tool”
One of the simplest ways to find your router’s public IP address is to use AstrillVPN’s IP checking tool. This tool detects your public IP automatically.
Click this link to the “What is my IP tool page. As soon as you land on the page, you’ll see your public IP address at the top.
Method 2: Accessing Your Router’s Web Interface
Most routers display your public IP address in the router’s admin interface. Here’s how you can find it:
- Open a web browser and type your router’s private IP (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into the address bar. Then, enter your login credentials (the username and password are typically on a sticker on the router).
- Once inside the router’s settings, navigate to the “Status” or “WAN” (Wide Area Network) section, where your public IP address will be listed.
Method 3: Using Command Prompt or Terminal (Windows and Mac)
You can use command-line tools to check for your public IP:
Windows
- Open Command Prompt and type nslookup myip.opendns.com resolver1.opendns.com. This command will return your public IP address using OpenDNS.
Mac/Linux
- Open Terminal and use the same command nslookup myip.opendns.com resolver1.opendns.com.
Method 4: Check Your Modem
If you’re using a modem provided by your ISP, it may display your public IP address directly. You can find this by:
- Logging into the modem’s web interface (similar to a router’s interface).
- Checking the WAN or Status section for the public IP information.
How to Find Xfinity Router IP Address?
To find the IP address of your Xfinity router, you can follow these methods:
Method 1: Using the Xfinity Router Web Interface
- Make sure your computer is connected to the Xfinity network (either via Wi-Fi or Ethernet).
- Open a web browser, and in the address bar, type 10.0.0.1, the default IP address for most Xfinity routers.
- For most Xfinity routers, the default username is “admin,” and the default password is “password.” If you’ve changed these credentials, use the updated ones.
Method 2: Using Command Prompt (Windows)
- Press Windows + R, type cmd, and press Enter to open Command Prompt.
- Type ipconfig and press Enter.
- Look for the section labeled “Default Gateway.” The number next to it is the IP address of your Xfinity router (typically 10.0.0.1).
Method 3: Using the Xfinity App
- Open the Xfinity My Account app on your smartphone.
- Tap on Internet and then tap on your network.
- Select Advanced Settings to see the router’s details, including the IP address.
Advantages of Configuring a VPN on Your Router
Setting up a VPN on your router offers numerous benefits that can significantly improve both the security and convenience of your home or office network. Here are the key advantages:
1. Network-Wide Protection
By configuring a VPN on your router, every device connected to your network benefits from VPN encryption. This includes devices that don’t support VPN apps, like smart TVs, gaming consoles, and IoT devices (smart speakers, cameras, etc.). All internet traffic from these devices will be encrypted, offering comprehensive protection across your network.
2. Constant VPN Connection
When a VPN is installed on a router, the VPN connection is always active. Unlike individual devices where you might forget to turn on the VPN, the router ensures that all traffic is consistently routed through the VPN tunnel. This eliminates the risk of unprotected browsing, providing continuous security and privacy.
3. Simplified Management
Instead of setting up and managing a VPN connection on each device, you only need to configure it once on the router. This centralized setup is more efficient, especially for large households or offices where many devices are connected simultaneously. The VPN will automatically cover any new device that joins the network without additional setup.
4. Bypass Regional Restrictions
A router VPN setup allows all devices on the network to bypass geo-blocks and access region-locked content. For example, if you set the VPN to a server in a specific country, all devices on your network will appear to be browsing from that location. This is ideal for streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, or BBC iPlayer or accessing services unavailable in your region.
5. Save Device Resources
Running a VPN on multiple devices can consume CPU and battery life resources. When the VPN is set up on the router, the router handles the encryption and decryption processes, freeing up resources on individual devices, particularly mobile ones.
6. Increased Privacy
A VPN hides your IP address from your ISP and other external parties, masking your online activities. With a VPN installed on your router, all devices are anonymized, making it much harder for third parties to track your entire network. This is especially useful if you’re concerned about surveillance or ISP tracking.
7. Comprehensive IoT Security
Many Internet of Things (IoT) devices, like smart thermostats or security cameras, cannot install a VPN directly, leaving them vulnerable to attacks. A router-based VPN ensures that all these devices benefit from encrypted connections, improving the overall security of your smart home.
8. Support for Multiple Devices
Most VPN services limit the number of simultaneous connections allowed. However, when the VPN is configured at the router level, it counts as only one connection, regardless of how many devices use it. This allows you to protect as many devices as needed under a single VPN subscription.
Why is AstrillVPN the best VPN for Routers?
AstrillVPN is often regarded as one of the best VPNs for routers due to its speed, security, advanced features, and wide compatibility. Here are some key reasons why AstrillVPN stands out for router use:
1. Extensive Router Compatibility
AstrillVPN is compatible with many routers, including popular brands such as Asus, Linksys, Netgear, and TP-Link. It supports routers with custom firmware like DD-WRT, Tomato, and AsusWRT-Merlin, making integrating AstrillVPN into most home or business network setups easy.
2. StealthVPN Protocol
One of AstrillVPN’s standout features is its StealthVPN protocol, which is particularly useful in bypassing VPN restrictions and firewalls, such as those imposed by governments or corporations. The StealthVPN protocol provides obfuscated VPN servers, allowing you to hide your VPN usage from ISPs and other prying eyes.
This protocol is highly effective for routers in regions like China, where internet censorship is prevalent. It allows you to access blocked websites and services while maintaining a stable connection across all devices in your network.
3. Fast and Reliable Speeds
AstrillVPN is known for delivering fast and stable speeds, even when using a VPN on a router, where speeds can sometimes be compromised due to encryption overhead. This is critical for bandwidth-heavy activities like streaming 4K content or gaming. Astrill’s ability to provide high-speed connections across its servers in 58 countries ensures that your entire network can handle data-intensive tasks without lag.
4. Strong Encryption and Privacy Features
With AES-256-bit encryption—the industry standard for secure VPN connections—AstrillVPN ensures that all data passing through your router is protected from hackers, snoopers, and other malicious actors. The VPN also has a no-logs policy, ensuring that none of your online activities are tracked or stored.
5. Site and App Filter
AstrillVPN’s site and app filter is particularly useful when using the VPN on a router. It allows you to selectively route certain traffic through the VPN while bypassing it for other sites or apps. This can improve performance for specific services, such as gaming or banking, that don’t need VPN encryption while still securing the rest of your network.
6. Multiple VPN Protocols
In addition to StealthVPN, AstrillVPN offers several other VPN protocols, including OpenVPN, WireGuard, and OpenWeb. These protocols offer flexibility depending on your needs: speed, security, or stealth. Multiple options are particularly useful when setting up a VPN on a router, as different networks or regions may require different protocols for optimal performance.
Does your IP Change when you Reset the Router?
Resetting a router can change your local IP address, but it doesn’t always change your public IP address. Here’s how it works:
Local IP Address
When you reset your router, it restores all settings to default, including the router’s internal IP address (often 192.168.1.1 or 10.0.0.1) and the IP addresses assigned to devices within your home network. These private IP addresses used for internal communications may change after a reset.
Public IP Address
The public IP address is assigned by your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and visible to the outside world. Resetting your router may or may not change your public IP address depending on the ISP’s policies:
- Dynamic IP Addresses: If your ISP assigns you a dynamic IP (which most ISPs do), your public IP address might change when the router reconnects to the network after a reset. However, this is not guaranteed, as ISPs often reassign the same IP address if the router reconnects quickly.
- Static IP Addresses: If you have a static IP, your public IP will remain the same even after resetting the router as your ISP fixes it.
FAQs
Your ISP assigns your Wi-Fi’s public IP address, which can be found by searching “What is my IP” on Google or visiting sites like WhatIsMyIP. The private IP address can be checked in your device’s network settings.
Yes, a router has a private IP address (e.g., 192.168.x.x for local network use) and a public IP address assigned by your ISP for internet access.
Log into your router’s web interface using its IP (e.g., 192.168.1.1), check the “Status” or “WAN” section, or use a ping test to check internet connectivity.



No comments were posted yet